When exploring why doesvoltagedropacross a resistor, it's essential to consider various aspects and implications. circuit analysis - Why doesvoltagedropacross a resistor .... You see a potential difference (voltage drop) across a resistor because the potential at the terminal of the resistor connected to the positive terminal of the power source has a higher potential than at the other terminal connected to the negative terminal of the power source. Understanding Voltage Drop Across a Resistor: A Practical Guide for .... Similarly, when a voltage drop occurs across a resistor, it results in energy being dissipated as heat, which can lead to a loss of power within the circuit.
This power loss affects the overall efficiency, as not all the electrical energy provided by the supply voltage is converted into useful work. How To Calculate A Voltage Drop Across Resistors - Sciencing. Sometimes, however, a drop in voltage can occur when there's not enough energy flowing through the circuit. In such cases, knowing how to calculate a voltage drop (loss of energy) across resistors can help you determine if a device isn't getting enough power to work properly.
Voltage drop - Wikipedia. In electronics, voltage drop is the decrease of electric potential along the path of a current flowing in a circuit. Voltage drops in the internal resistance of the source, across conductors, across contacts, and across connectors are undesirable because some of the energy supplied is dissipated. Does voltage drop across a resistor? This perspective suggests that, voltage drop happens across a resistor.

According to Ohm's Law, the voltage drop (V) across a resistor is directly proportional to the current (I) flowing through it and the resistance (R) of the resistor. Voltage Drop: Causes and Solutions - Electrical4uonline. Resistance: Every wire, cable, or component in a circuit has some resistance.
As current flows through the circuit, it encounters this resistance, which reduces the voltage. The higher the resistance, the greater the voltage drop. What Is a Voltage Drop in an Electric Circuit?. When current is flowing through a resistor, we can measure the amount of work (per unit charge) required to keep the current flowing through the resistor.
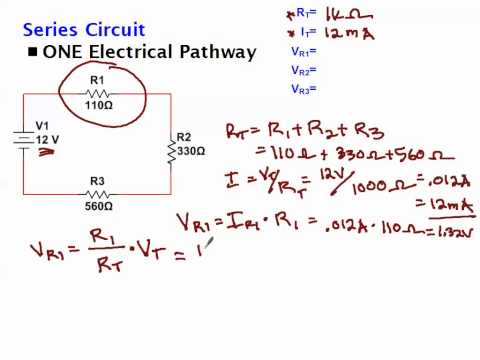
This is the essence of voltage drop: a battery (or voltage source) supplies energy for doing the work of moving charge. Voltage drop across a single resistor and across two resistors. Now, I know the theory and how to apply Ohm's law.
The question is why does the voltage drop across resistors of the same resistance vary from the first circuit to the second circuit? Does it have anything to do with current? Moreover, i am trying to find an intuitive explanation as to why it happens. Explaination of voltage drop across resistors - Physics Forums. The discussion centers on understanding why voltage increases across a resistor as resistance increases, as described by Ohm's law.

It clarifies that while resistance does not increase with voltage, a larger resistance requires more work to push current through, resulting in a larger voltage drop. What is voltage drop exactly?

📝 Summary
Learning about why does voltage drop across a resistor is valuable for those who want to this subject. The information presented above works as a valuable resource for continued learning.
Whether you're new to this, or knowledgeable, one finds something new to learn about why does voltage drop across a resistor.
