The subject of eukaryotes vs prokaryotes chart encompasses a wide range of important elements. Eukaryote - Wikipedia. All animals, plants, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryote | Definition, Structure, & Facts | Britannica. It's important to note that, eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus.
From another angle, the eukaryotic cell has a nuclear membrane that surrounds the nucleus, in which the well-defined chromosomes (bodies containing the hereditary material) are located. Learn more about eukaryotes in this article. Eukaryotic Cell – Diagram, Definition, Facts.
Cells are the smallest units of life, and they come in two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Eukaryotic cells are structurally more complex, with a nucleus that contains DNA and organelles that perform specialized functions. Building on this, prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes: Key Cell Differences | Osmosis.

What is a eukaryotic cell? A eukaryotic cell, or a cell that contains membrane-bound structures, is the basis for every multicellular organism, including animals, plants, and humans as well as some unicellular organisms (organisms with a single cell), such as protozoa. Eukaryote - Definition and Types | Biology Dictionary. Eukaryotes are organisms whose bodies are made up of eukaryotic cells, such as protists, fungi, plants and animals. Eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a nucleus and organelles, and are enclosed by a plasma membrane.
Eukaryotic Cells: Eukaryote Definition and Structure | Technology Networks. Eukaryotic cells form the foundation of complex life. This article details the structure of eukaryotic cells and provides examples of eukaryotes. Eukaryotic Cell: Definition, Structure, & Examples - Science Facts. Eukaryotic cells are defined as cells that contain an organized nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.

They have a more advanced structural organization that is large and more complex than a prokaryotic cell. However, they share a few common features, including the cytoplasm. Animals are eukaryotes that distinct from the other groups of eukaryotes by being heterotrophic, motile, and multicellular, a body organized into cells, tissues, organs, and systems, lacking cell walls and chloroplasts, and growing from a blastula during embryonic development. Eukaryote - New World Encyclopedia.
Eukaryotes comprise animals, plants, and fungi —which are mostly multicellular—as well as various other groups that are collectively classified as protists (many of which are unicellular). eukaryote / eucariote | Learn Science at Scitable - Nature. Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. There is a wide range of eukaryotic organisms, including all animals, plants, fungi, and protists, as...
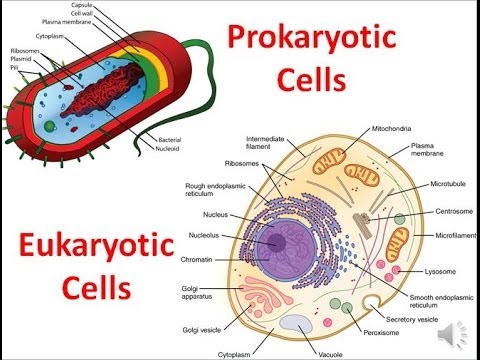

📝 Summary
As we've seen, eukaryotes vs prokaryotes chart represents an important topic worth exploring. Going forward, further exploration in this area may yield even greater understanding and value.
It's our hope that this article has offered you useful knowledge about eukaryotes vs prokaryotes chart.
