What Is Pointer Pdf Pointer Computer Programming Integer
Pointer In C Programming Pdf Pointer Computer Programming C A pointer is a variable that stores the memory address of another variable. instead of holding a direct value, it holds the address where the value is stored in memory. it is the backbone of low level memory manipulation in c. accessing the pointer directly will just give us the address that is stored in the pointer. for example,. Pointers introduction what is a pointer? • simple variables: an int float variable is like a box which can store a single int value such as 42. • pointer does not store a simple value directly. instead, a pointer stores a reference to another value. a pointer variable. the current value is a reference to the pointee num above.

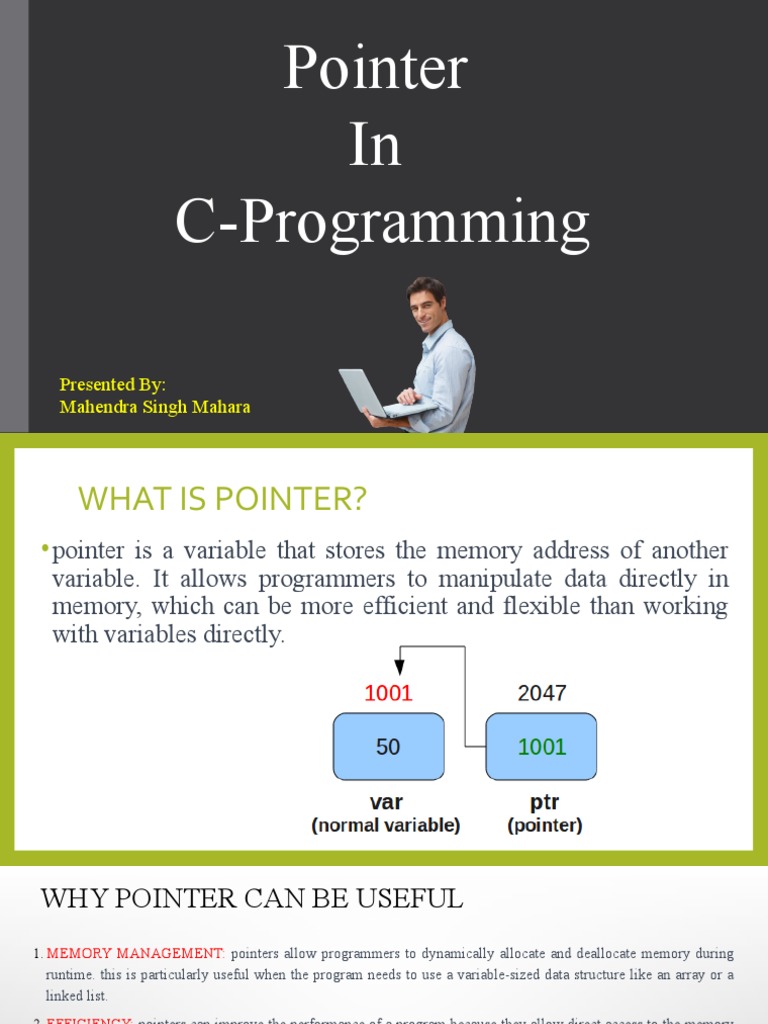
Pointer Pdf Pointer Computer Programming Integer Computer Science A pointer in c is a variable that stores the address of another variable, allowing for efficient data manipulation and dynamic memory allocation. pointers are declared using the '*' operator and initialized with the address of a variable using the '&' operator. Pointer (computer programming) in computer science, a pointer is an object in many programming languages that stores a memory address. this can be that of another value located in computer memory, or in some cases, that of memory mapped computer hardware. Now let us see what is a pointer. what are pointers? a pointer is a variable whose value is the address of another variable, i.e., direct address of the memory location. like any variable or constant, you must declare a pointer before you can use it to store any variable address. the general form of a pointer variable declaration is:. Pointer arithmetic provides an alternative to array indexing in c. the two statements: ptr = a 1; and ptr = &a[1]; are equivalent and would assign the value of 404 to ptr.

What Is Pointer Pdf Pointer Computer Programming Integer Now let us see what is a pointer. what are pointers? a pointer is a variable whose value is the address of another variable, i.e., direct address of the memory location. like any variable or constant, you must declare a pointer before you can use it to store any variable address. the general form of a pointer variable declaration is:. Pointer arithmetic provides an alternative to array indexing in c. the two statements: ptr = a 1; and ptr = &a[1]; are equivalent and would assign the value of 404 to ptr. A pointer variable is declared by giving it a type and a name (e.g. int *ptr) where the asterisk tells the compiler that the variable named ptr is a pointer variable and the type tells the compiler what type the pointer is to point to (integer in this case). Pointers are more "low level" than arrays and reference variables. this means you are responsible for finding the address you want to store in the pointer and correctly using it. the indirection operator (*) dereferences a pointer. it allows you to access the item that the pointer points to. this prints 25. For example, an integer variable holds (or you can say stores) an integer value, however an integer pointer holds the address of a integer variable. in this guide, we will discuss pointers in c programming with the help of examples. 22 int sum(elementtype v[], int num, elementgetvalue gv) { int temp sum; int i; temp sum = 0; for (i=0; i
Comments are closed.