What Are The Future Use Cases For Blockchain Technology

Blockchain Future 2 The Expected Future Use Cases Of Blockchain The class template std::future provides a mechanism to access the result of asynchronous operations: an asynchronous operation (created via std::async, std::packaged task, or std::promise) can provide a std::future object to the creator of that asynchronous operation. the creator of the asynchronous operation can then use a variety of methods to query, wait for, or extract a value from the std. A future statement is a directive to the compiler that a particular module should be compiled using syntax or semantics that will be available in a specified future release of python. the future statement is intended to ease migration to future versions of python that introduce incompatible changes to the language. it allows use of the new features on a per module basis before the release in.

Future Use Cases And The Impact Of Blockchain The get member function waits (by calling wait ()) until the shared state is ready, then retrieves the value stored in the shared state (if any). right after calling this function, valid () is false. if valid () is false before the call to this function, the behavior is undefined. The first part is easy: you can use annotations because annotations have existed since python 3.0, you don't need to import anything from future to use them what you're importing if you do from future import annotations is postponed annotations. the postponed annotations feature means that you can use something in an annotation even if it hasn't been defined yet try the following: def. Checks if the future refers to a shared state. this is the case only for futures that were not default constructed or moved from (i.e. returned by std::promise::get future (), std::packaged task::get future () or std::async ()) until the first time get () or share () is called. the behavior is undefined if any member function other than the destructor, the move assignment operator, or valid is. An unwrapping constructor from future

Future Use Cases And The Impact Of Blockchain Checks if the future refers to a shared state. this is the case only for futures that were not default constructed or moved from (i.e. returned by std::promise::get future (), std::packaged task::get future () or std::async ()) until the first time get () or share () is called. the behavior is undefined if any member function other than the destructor, the move assignment operator, or valid is. An unwrapping constructor from future
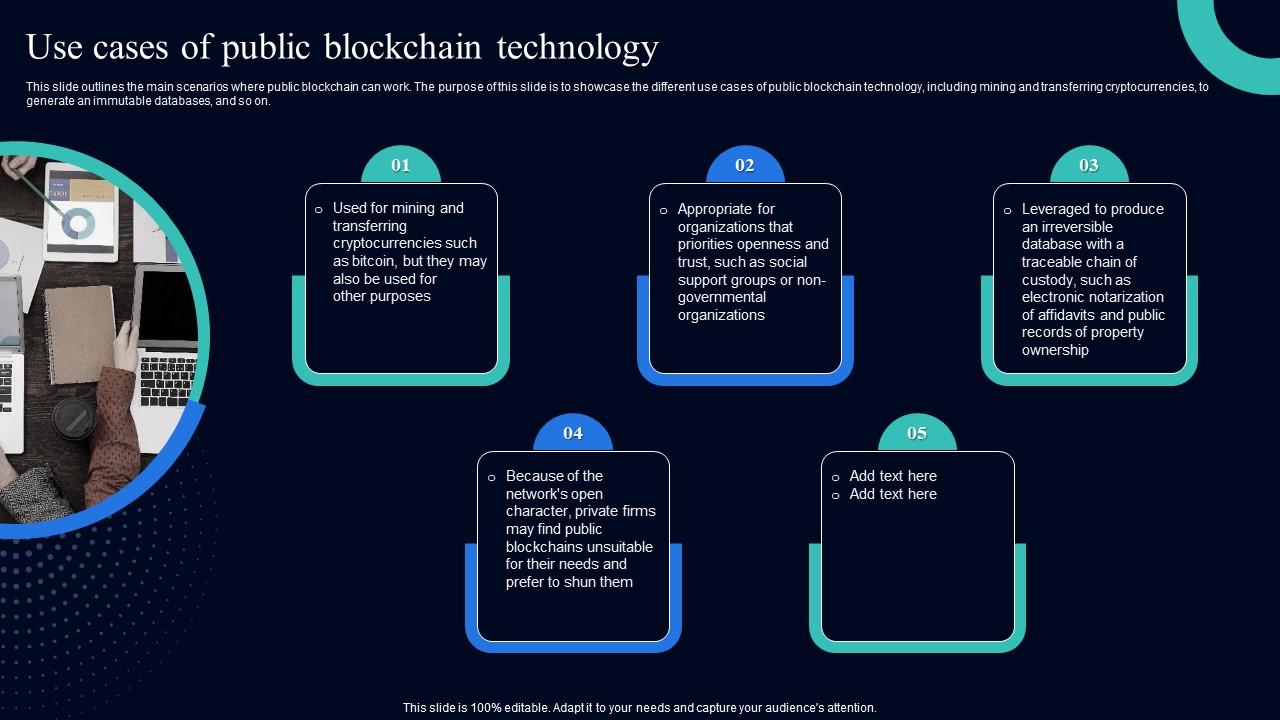
Use Cases Of Public Blockchain Technology Blockchain Use Cases It Ppt The return type of std::async is std::future
Comments are closed.