What Are Scalar And Vector Quantities Revise Gcse Physics With

Vector And Scalar Quantities Gcse Physics Teaching Resources Scalar quantities can be subtracted by subtracting one value from another. a room is heated from 12°c to 21°c using a radiator. calculate the increase in temperature. 21°c 12°c = 9°c. learn. Learn about scalar and vector quantities for your gcse physics exam. this revision note covers examples of scalars and vectors, and how to represent vectors.

Vector And Scalar Quantities Gcse Physics Teaching Resources This section explains forces: scalar and vector quantities, covering, contact and non contact forces, gravity, weight calculation formula, resultant forces and work done and energy transfer. Scalar quantities have magnitude (size) only. scalar quantities do not have a direction. displacement is a vector quantity. displacement is distance in a specific direction. example : vector quantity. in our journey in figure 1 we have travelled a distance of 800m. our displacement is 500m due west from our starting point. Scalar quantities are physical quantities that have a magnitude but no direction. they are measured with a numerical value. some examples of scalar quantities are: vector quantities are different from scalar quantities because they have both magnitude and direction. some examples of vector quantities are:. Vector quantities have magnitude and associated direction. some things, like forces and velocity, can be measured by magnitude and direction. for example, velocity tells us the speed and direction of travel. we need to know 6 main vectors for aqa exams. these are weight, force, momentum, acceleration, displacement and velocity.

Gcse Aqa Physics Forces 4 5 1 1 Scalar And Vector Quantities Scalar quantities are physical quantities that have a magnitude but no direction. they are measured with a numerical value. some examples of scalar quantities are: vector quantities are different from scalar quantities because they have both magnitude and direction. some examples of vector quantities are:. Vector quantities have magnitude and associated direction. some things, like forces and velocity, can be measured by magnitude and direction. for example, velocity tells us the speed and direction of travel. we need to know 6 main vectors for aqa exams. these are weight, force, momentum, acceleration, displacement and velocity. The direction of movement shows the difference between a scalar and vector quantity. examples of vector quantities used in physics (from top): force, displacement, acceleration, weight. What is the difference between a scalar and a vector? a scalar (pronounced scay lar) only has magnitude (size). a vector has both magnitude and direction. examples of scalars are. density, energy, length, mass, power, speed and temperature. examples of vectors are. acceleration, displacement, force, momentum, velocity and weight. Are the following quantities scalar or vector: force, weight and acceleration? everything you need to know about scalars and vectors for the gcse physics (combined science) aqa exam, totally free, with assessment questions, text & videos. Vector quantities have both a magnitude and a direction, whereas scalar quantities have only a magnitude.

Gcse Aqa Physics Forces Scalar And Vector Quantities Teaching Resources The direction of movement shows the difference between a scalar and vector quantity. examples of vector quantities used in physics (from top): force, displacement, acceleration, weight. What is the difference between a scalar and a vector? a scalar (pronounced scay lar) only has magnitude (size). a vector has both magnitude and direction. examples of scalars are. density, energy, length, mass, power, speed and temperature. examples of vectors are. acceleration, displacement, force, momentum, velocity and weight. Are the following quantities scalar or vector: force, weight and acceleration? everything you need to know about scalars and vectors for the gcse physics (combined science) aqa exam, totally free, with assessment questions, text & videos. Vector quantities have both a magnitude and a direction, whereas scalar quantities have only a magnitude.
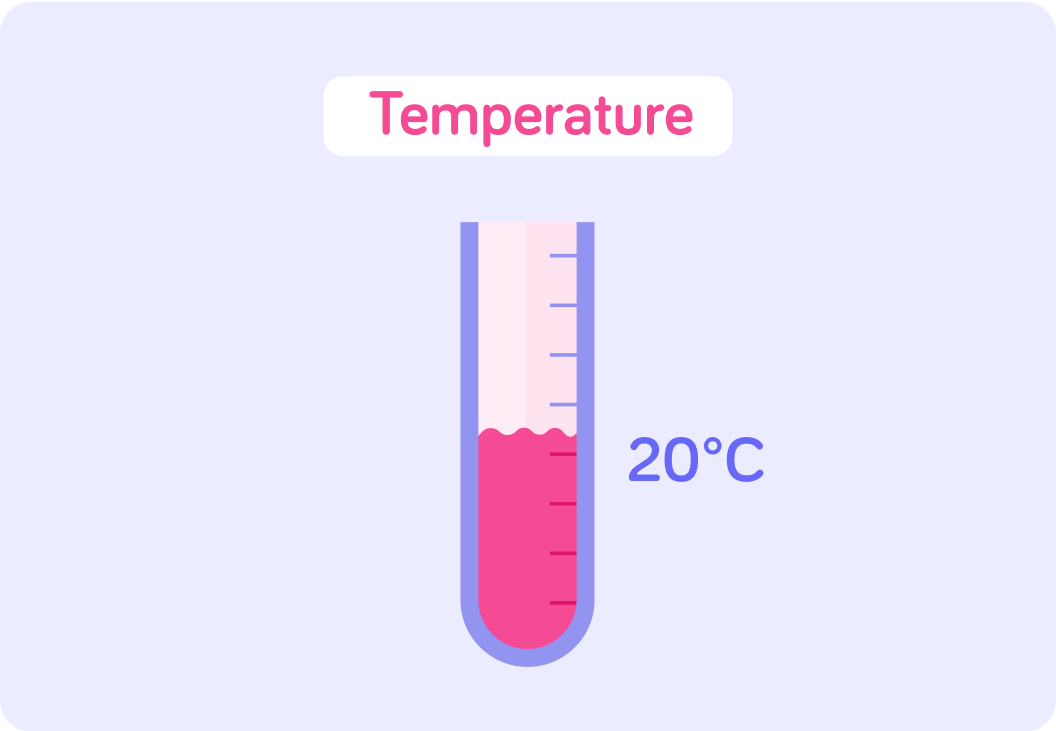
What Are Scalar And Vector Quantities Revise Gcse Physics With Are the following quantities scalar or vector: force, weight and acceleration? everything you need to know about scalars and vectors for the gcse physics (combined science) aqa exam, totally free, with assessment questions, text & videos. Vector quantities have both a magnitude and a direction, whereas scalar quantities have only a magnitude.
Comments are closed.