Understanding Successive Approximation Type Adc Basics Structure And
Understanding Successive Approximation Type Adc Basics Structure And Find info on the basics of successive approximation register (sar) analog to digital converters (adcs). review sar adc with pipeline, flash, and sigma delta adcs. The basic principle of this type of a d converter is that the unknown analog input voltage is approximated against an n bit digital value by trying one bit at a time, beginning with the msb. the principle of successive approximation process for a 4 bit conversion is explained here.

Successive Approximation Adc Download Free Pdf Analog To Digital One of the most common analog to digital converters used in applications requiring a sampling rate under 10 msps is the successive approximation register adc. this adc is ideal for applications requiring a resolution between 8 16 bits. What is a successive approximation adc? the successive approximation adc is the adc of choice for low cost medium to high resolution applications, the resolution for sar adcs ranges from 8 18 bits, with sample speeds up to 5 mega samples per second (msps). Sar, stands for successive approximation register. the name refers to the process where cdac is adjusted in successive approximations to tr and match the voltage stored in the sample in hold. the word register refers to the fact that the res. In this tutorial, you will explore the fundamentals of successive approximation type adcs, including their definition, key features, and construction. you will also learn how a 4 bit sar adc operates, understand the calculation of conversion time, and examine the advantages and disadvantages of sar adcs.
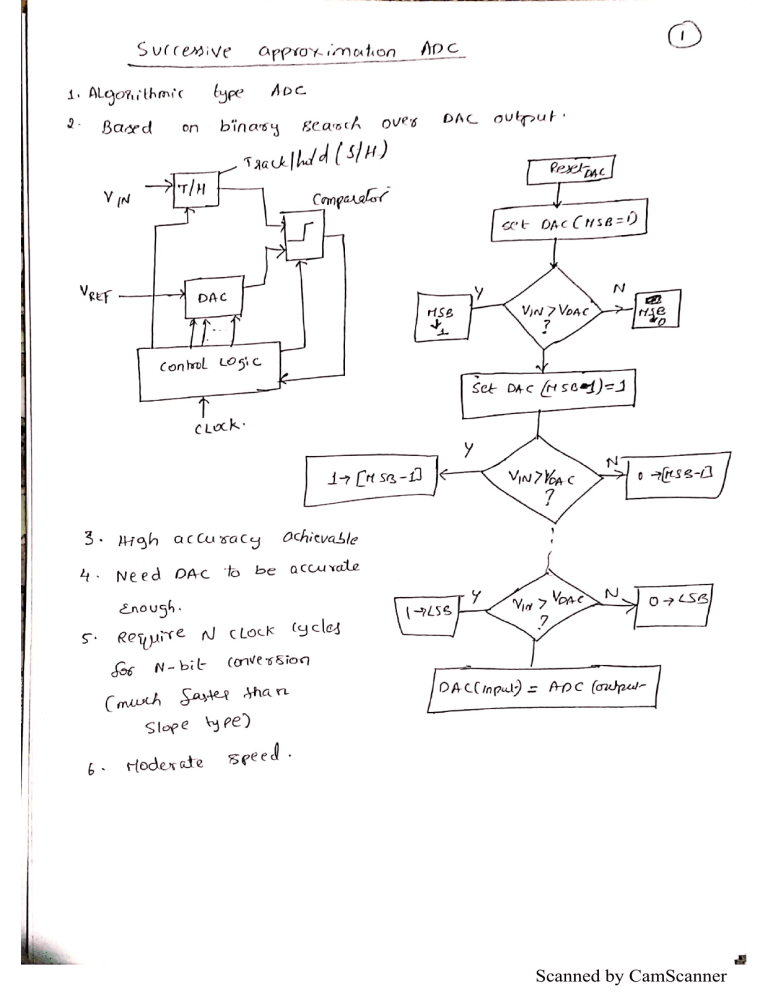
Successive Approximation Adc Notes Sar, stands for successive approximation register. the name refers to the process where cdac is adjusted in successive approximations to tr and match the voltage stored in the sample in hold. the word register refers to the fact that the res. In this tutorial, you will explore the fundamentals of successive approximation type adcs, including their definition, key features, and construction. you will also learn how a 4 bit sar adc operates, understand the calculation of conversion time, and examine the advantages and disadvantages of sar adcs. This blog post provides a comprehensive overview of the successive approximation type analog to digital converter (adc), covering its basics, structure, working mechanism, conversion process, and advantages over other types of adcs. The successive approximation analog to digital converter (sar adc) circuit is typically composed of four primary subcircuits: an analog voltage comparator that compares v in with the output of the internal dac and conveys the comparison result to the successive approximation register (sar). It covers the basic introduction of adc, its workings, and moves towards successive approximation adc. then we discuss the example along with its workings, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Abstract: successive approximation register (sar) analog to digital converters (adcs) represent the majority of the adc market for medium to high resolution adcs. sar adcs provide up to 5msps sampling rates with resolutions from 8 to 18 bits.

Successive Approximation Type Adc Electronics Engineering Study Center This blog post provides a comprehensive overview of the successive approximation type analog to digital converter (adc), covering its basics, structure, working mechanism, conversion process, and advantages over other types of adcs. The successive approximation analog to digital converter (sar adc) circuit is typically composed of four primary subcircuits: an analog voltage comparator that compares v in with the output of the internal dac and conveys the comparison result to the successive approximation register (sar). It covers the basic introduction of adc, its workings, and moves towards successive approximation adc. then we discuss the example along with its workings, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Abstract: successive approximation register (sar) analog to digital converters (adcs) represent the majority of the adc market for medium to high resolution adcs. sar adcs provide up to 5msps sampling rates with resolutions from 8 to 18 bits.
Comments are closed.