Understanding Measuring Compression Ratio Static Dynamic Effective Two Four Stroke

Compression Ratio Explained Static Dynamic Pdf Internal Static and dynamic (or corrected and uncorrected) as well as effective (boost) compression ratios are explained for both two stroke and four stroke engines. Dynamic compression ratio (dcr) is an important concept in high performance engines. determining what the compression ratio is after the intake valve closes provides valuable information about how the engine will perform with a particular cam and octane.

Determining Compression And Fuel Ratios For A Modified 4 Stroke Engine Compression ratios, including static uncorrected, dynamic corrected, and effective boost, are explained. then details are given about measuring and calculating compression ratios for two stroke. Dcr can be used to determine a compression pressure ratio which allows the computation of thermal efficiency. compression pressure and temperature. and those inlet conditions will change with throttle, resonant. induction tuning, boost and temperature. does camshaft ivc timing affect dcr? yes, indeed it does. dcr is shown in red. Compression ratios are fundamental to enhancing engine performance, understanding both static and dynamic compression ratios can give you an edge in fine tuning your vehicle's performance using hp tuners products. let's discuss what they are and how they play a role in tuning. Check to see what your static and dynamic compression is based on engine parameters. the compression ratio is simply the ratio of the uncompressed volume in the cylinder to the compressed volume. the compressed volume for the dynamic compression ratio is the same as the static compression ratio.

Effects Of Effective Stroke Length To Bore Ratio To Dimensionless Compression ratios are fundamental to enhancing engine performance, understanding both static and dynamic compression ratios can give you an edge in fine tuning your vehicle's performance using hp tuners products. let's discuss what they are and how they play a role in tuning. Check to see what your static and dynamic compression is based on engine parameters. the compression ratio is simply the ratio of the uncompressed volume in the cylinder to the compressed volume. the compressed volume for the dynamic compression ratio is the same as the static compression ratio. You need to select a cam duration and lsa , and static compression that both matches the static compression ratio and your cars gearing so the effective dynamic compression ratio falls in that range, and intended rpm power band. Static is meaningful, calculated by measuring actual volumes (cc) of the piston's domes reliefs, chamber and head gasket along with measuring the bore, stroke and deck. For four stroke engines it is standard practice to calculate compression ratio based on the full swept volume of the engine. this is often referred to as "geometric compression ratio" but is also known as the "static compression ratio". Motor needs more static compression ratio or less cam. keeping the scr the same, the motor needs a cam that closes the intake at 25 degrees abdc @0.050" tappet lift, which would produce a 7.93:1 dcr.
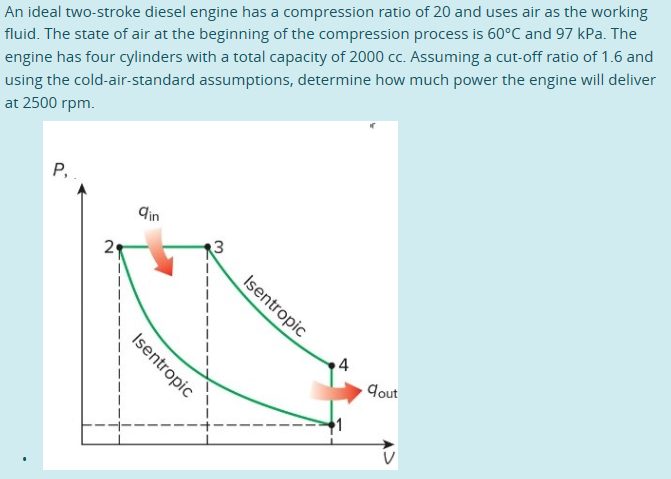
Solved An Ideal Two Stroke Diesel Engine Has A Compression Chegg You need to select a cam duration and lsa , and static compression that both matches the static compression ratio and your cars gearing so the effective dynamic compression ratio falls in that range, and intended rpm power band. Static is meaningful, calculated by measuring actual volumes (cc) of the piston's domes reliefs, chamber and head gasket along with measuring the bore, stroke and deck. For four stroke engines it is standard practice to calculate compression ratio based on the full swept volume of the engine. this is often referred to as "geometric compression ratio" but is also known as the "static compression ratio". Motor needs more static compression ratio or less cam. keeping the scr the same, the motor needs a cam that closes the intake at 25 degrees abdc @0.050" tappet lift, which would produce a 7.93:1 dcr.
Comments are closed.