Statistical Theory Of Quantization Pdf Sampling Signal Processing
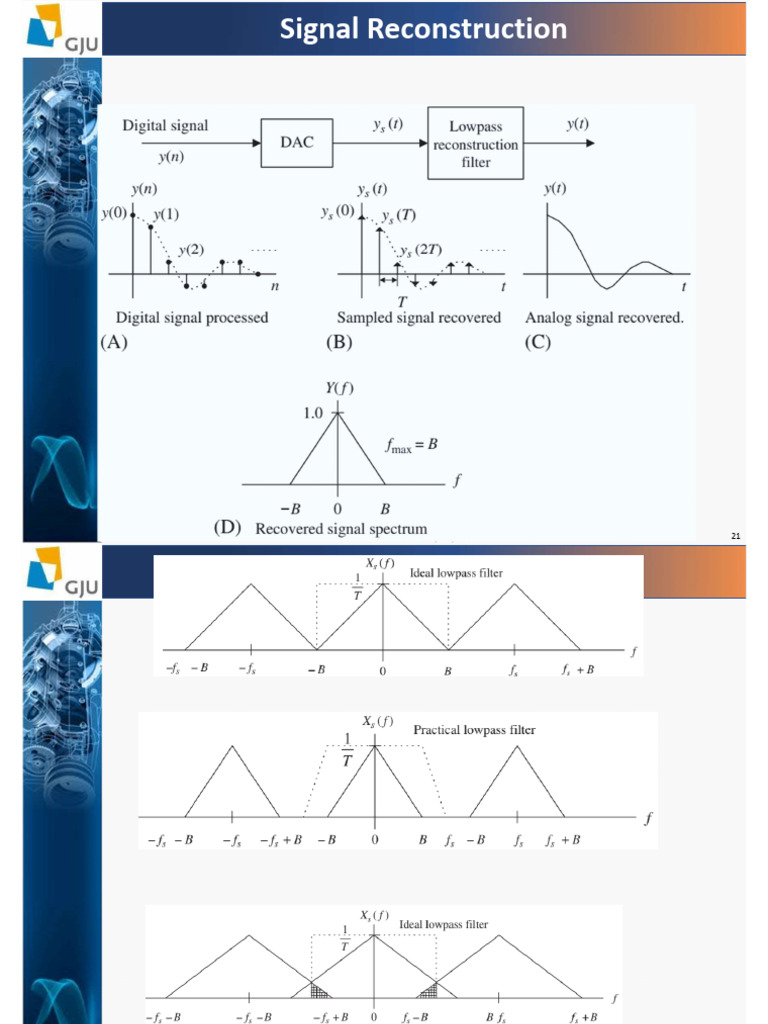
Signal Sampling And Quantization 3 Pdf Sampling Signal In fact, we will show how linear system theory can be precisely used to analyze the effect of quantization on moments and other statistical properties of the signals. sampling discretizes time, and quantization discretizes am plitude. The process of digitizing the domain is called sampling and the process of digitizing the range is called quantization. most devices we encounter deal with both analog and digital signals. digi tal signals are particularly robust to noise, and extremely efficient and versatile means for processing digital signals have been developed.

Signal Sampling Quantization Binary Encoding Oleh Albert Sagala This document discusses the statistical theory of quantization in digital signal processing. [1] quantization discretizes the amplitude of a continuous signal, similarly to how sampling discretizes time. [2]. In our motivation, we presented two mappings (on the lhs). they can be summarized using the scheme on the rhs. student 1: generates samples at every 5 seconds. each sample is a real number between 10 and 10 chosen at random. student 2: maps each sample to a bit and transmits that bit to the receiver over the communication channel. Careful study of quantization reveals that the pdf's of the input and output signals are related to each other through a special type of sampling. the output pdf is a string of dirac delta functions whose areas correspond to the areas under the input pdf within the bounds of each quantum box. A b bit quantizer can map a signal into 2b levels. sampling quantization s & q for l intervals we need [log2l] bits or nearest larger integer. sampling at fs samples sec., the bit rate is r = fs⌈log2l⌉bits sec. consider the quantizer: let msqei be the mean squared quantization error when sample is in the ith quantization interval.
New Material Image Sampling And Quantization Pdf Sampling Signal Careful study of quantization reveals that the pdf's of the input and output signals are related to each other through a special type of sampling. the output pdf is a string of dirac delta functions whose areas correspond to the areas under the input pdf within the bounds of each quantum box. A b bit quantizer can map a signal into 2b levels. sampling quantization s & q for l intervals we need [log2l] bits or nearest larger integer. sampling at fs samples sec., the bit rate is r = fs⌈log2l⌉bits sec. consider the quantizer: let msqei be the mean squared quantization error when sample is in the ith quantization interval. Sampling theorem sampling theorem: a signal g(t) with bandwidth < can be reconstructed exactly from samples taken at any rate r > 2b sampling can be achieved mathematically by multiplying by an impulse train. Derivation of pdf of x’ from area sampling of the pdf of z: (a) pdf of 2; (b) rectangular pulse function; (c) convolution of (a) and (b); (d) the impulse train; and (e) pdf of z’, the product of (c) and (d). In sampling, we convert continuous–time analog signals (signals that are defined at all time instants and have amplitudes that may take any real value) to discrete–time analog signals (signals that are defined at specific instants of time but still have amplitudes that may take any real value). Some practical considerations: input output quantization. filter coefficient quantization. product roundoff. potential overflow in sums. our nice simple lti system is now highly nonlinear. in general, nonlinear systems like this are difficult to analyze.

Lecture 4 Quantization Pdf Analog To Digital Converter Sampling Sampling theorem sampling theorem: a signal g(t) with bandwidth < can be reconstructed exactly from samples taken at any rate r > 2b sampling can be achieved mathematically by multiplying by an impulse train. Derivation of pdf of x’ from area sampling of the pdf of z: (a) pdf of 2; (b) rectangular pulse function; (c) convolution of (a) and (b); (d) the impulse train; and (e) pdf of z’, the product of (c) and (d). In sampling, we convert continuous–time analog signals (signals that are defined at all time instants and have amplitudes that may take any real value) to discrete–time analog signals (signals that are defined at specific instants of time but still have amplitudes that may take any real value). Some practical considerations: input output quantization. filter coefficient quantization. product roundoff. potential overflow in sums. our nice simple lti system is now highly nonlinear. in general, nonlinear systems like this are difficult to analyze.
Comments are closed.