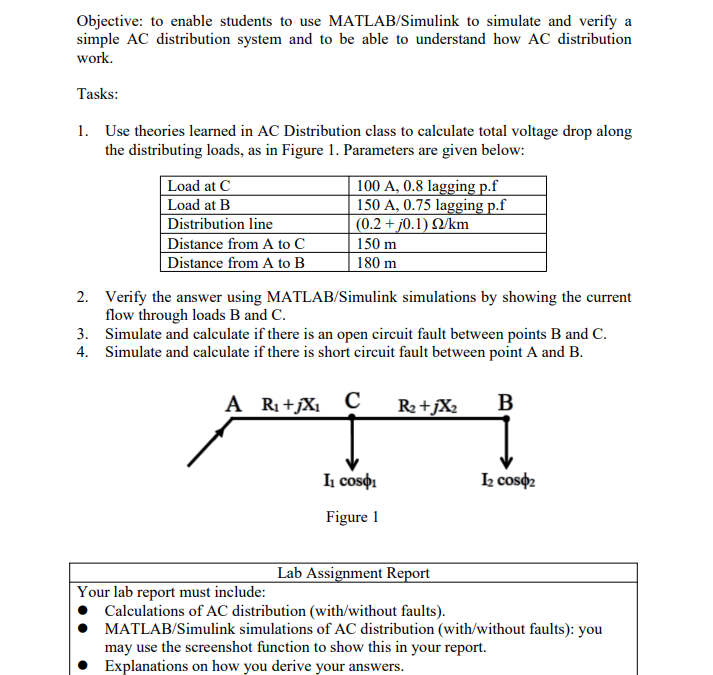
Solved Practice What Type Of Interactions Are Present In Chegg

Solved Practice What Type Of Interactions Are Present In Chegg Practice: what type of interactions are present in these molecules? your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: practice: what type of interactions are present in these molecules? there are 3 steps to solve this one. van der waals forces are wea. The type of inter molecular interactions present in (a)methanol and acetone (i)van der waal’s forces of attraction (b)acetonitrileand acetone (ii)ion dipole interaction (iii)dipole dipole interaction (a) (b)1. (iii) (ii) 2. (ii) (ii)3. (iii) (iii)4. (iii) (i) ncert exercise based mcqs solutions chemistry neet practice questions, mcqs, past year questions (pyqs), ncert questions, question.

Solved Question Chegg Identify the different types of attractive forces or interactions present in the given tertiary structure of a protein molecule. drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Ask any question and get an answer from our subject experts in as little as 2 hours. Enhanced with ai, our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. which of the following interactions are present between molecules? here’s the best way to solve it. we must distinguish between the different types of intermolecular forces that can exist between mole. 12.6 what kinds of intermolecular forces are involved in solution formation? 12.7 explain how the relative strengths of solute solute interactions, solvent solvent interactions, and solvent solute interactions affect solution formation.

Solved Practice 1 Predict What Type Of Interactions Each Chegg Enhanced with ai, our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. which of the following interactions are present between molecules? here’s the best way to solve it. we must distinguish between the different types of intermolecular forces that can exist between mole. 12.6 what kinds of intermolecular forces are involved in solution formation? 12.7 explain how the relative strengths of solute solute interactions, solvent solvent interactions, and solvent solute interactions affect solution formation. Q: consider the scheme for the multistep synthesis below. what types of reactions transformations are needed to convert the reagent to the major product. does the sequence matter?. Chem 121 practice worksheet #8 1) which type of intermolecular interaction would be the strongest in each substance (between molecules of the same substance)? it may help to draw the lewis structures first. Identify the type or types of intermolecular forces present between molecules of the compound pictured below: this molecule is polar, and it has a hydrogen covalently bonded to a nitrogen. therefore, dispersion forces, dipole dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding are all present. Interactions, solvent solvent interactions, and solute solute interactions. show all three types in your sketches!.
Solved Question Chegg Q: consider the scheme for the multistep synthesis below. what types of reactions transformations are needed to convert the reagent to the major product. does the sequence matter?. Chem 121 practice worksheet #8 1) which type of intermolecular interaction would be the strongest in each substance (between molecules of the same substance)? it may help to draw the lewis structures first. Identify the type or types of intermolecular forces present between molecules of the compound pictured below: this molecule is polar, and it has a hydrogen covalently bonded to a nitrogen. therefore, dispersion forces, dipole dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding are all present. Interactions, solvent solvent interactions, and solute solute interactions. show all three types in your sketches!.
Comments are closed.