Solved No Lsa Type 2 For Stubs Links Cisco Community

Solved No Lsa Type 2 For Stubs Links Cisco Community Type 2 network lsa is listed by r1 as 1 link count in router link states section and then as type 2 right after. this is called transit network refers as pseudonode as ospf cannot show 2 and more routers connected to shared medium where election is held. In ospf database, a point to point link is modelled actually as two entries in lsa1: one entry describes solely a direct connection to another router, without advertising the network that is present on the link. the second entry advertises the network on the point to point link as a stub network.

Solved Cisco Acs Server 5 8 0 32 Report Blank Page Cisco Community This lesson explains the ospf lsa types and where we encounter them. we also look how to check them on cisco ios routers. Without lsa 3, it would be impossible for a stubby area to have a default route to other areas, and would be in effect isolated from the rest of the network. what happens, however, is that abrs in totally stubby areas do not originate any other lsa 3 for other inter area networks. In this ospf lsa types lessob, we will learn ospf lsa type 1, type 2, type 3, type 4, type 5 and ospf lsa types like opaque lsas. Correct, no lsa type 5 7 are allowed in stub area, so no external routes are allowed. even if that would not seem efficient, in some toplogy that would help devices resources to be less burdened, in fact the main purpose of the stub areas would be to replace the external lsas with a default route.

What Does The Link Type In The Lsa Type 1 Mean Cisco Community In this ospf lsa types lessob, we will learn ospf lsa type 1, type 2, type 3, type 4, type 5 and ospf lsa types like opaque lsas. Correct, no lsa type 5 7 are allowed in stub area, so no external routes are allowed. even if that would not seem efficient, in some toplogy that would help devices resources to be less burdened, in fact the main purpose of the stub areas would be to replace the external lsas with a default route. The area 0 to nssa abr acts as a firewall for lsa type 5 in area 0.0.0.0 and doesn t allow them to enter the nssa link state database. lsa type 7 may be converted to lsa type 5 or not depending on the setting of the p bit from the nssa abr. Type 2 lsa’s are present on a multi access link – a dr exclusively generates type 2 lsas and the tell the other routers about the network and the routers connected to them. both lsa types 1 and 2 exist in all areas and are never flooded outside of the area. The purpose of the network lsa is to list the ospf routers that are connected to the common segment of the dr and it actually lists the ospf rids and not the lan ip addresses of the nodes connected to the dr pseudonode. R2 receives the type 2 lsa's r1 and detects that r3 is located in the same subnet and can be reached directly. r3 advertises to r1 a type 1 lsa with its own rid 0.0.0.3 as a link state id and listing in the body's lsa two links.
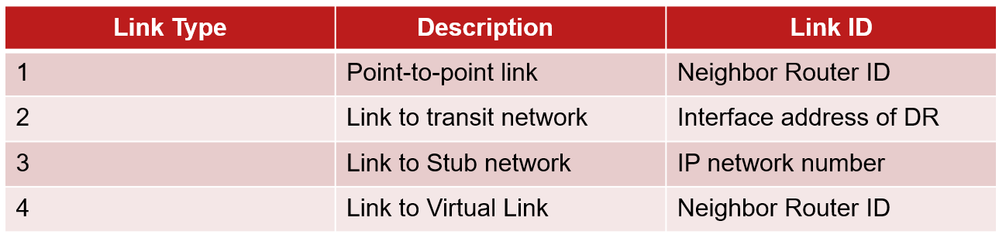
What Does The Link Type In The Lsa Type 1 Mean Cisco Community The area 0 to nssa abr acts as a firewall for lsa type 5 in area 0.0.0.0 and doesn t allow them to enter the nssa link state database. lsa type 7 may be converted to lsa type 5 or not depending on the setting of the p bit from the nssa abr. Type 2 lsa’s are present on a multi access link – a dr exclusively generates type 2 lsas and the tell the other routers about the network and the routers connected to them. both lsa types 1 and 2 exist in all areas and are never flooded outside of the area. The purpose of the network lsa is to list the ospf routers that are connected to the common segment of the dr and it actually lists the ospf rids and not the lan ip addresses of the nodes connected to the dr pseudonode. R2 receives the type 2 lsa's r1 and detects that r3 is located in the same subnet and can be reached directly. r3 advertises to r1 a type 1 lsa with its own rid 0.0.0.3 as a link state id and listing in the body's lsa two links.
Comments are closed.