Solved Let A 1 2 3 4 5 And B 0 3 6 Find A B Chegg

Solved Let A 1 2 3 4 5 And B 0 3 6 Find A B Chegg Your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. see answer. To solve the operations with the sets a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and b = {0, 3, 6}, we use the definitions of set union, intersection, and difference. union: finding the union of two sets (a ∪ b) involves combining all unique elements from both sets.

Solved Let A 1 2 3 4 5 And B 0 3 6 Find A Aв єb B Aв B Chegg A = \ {1, 2, 3, 4, 5\}a= {1,2,3,4,5} and b = \ {0, 3, 6\}b = {0,3,6} find the union of sets aa and bb, which includes all elements that are in aa, in bb, or in both. To solve this problem, we are given two sets, a and b: a= {1,2,3,4,5}b ={0,3,6} we have to find the union, intersection, difference, and symmetric difference of the sets. step 1. find the union of sets a and b. the union of two sets a and b, denoted by a∪b, is the set that contains all the elements of a and b without repetition. Find a – b and b – a. a – b = a – (a ∩ b) a ∩ b = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} ∩ {2, 4, 6, 8} = {2, 4, 6} a – b = a – (a ∩ b) = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} – {2, 4, 6} = {1, 3, 5} b – a = b – (b ∩ a) = b – (a ∩ b) = {2,. To solve the problem step by step, we will follow the instructions given in the question. the intersection a′∩b′ consists of elements that are common to both a′ and b′. the union a∪b consists of all elements that are in either a or b or in both. the complement of a∪b is defined as the universal set u minus the elements of a∪b.

Solved Let A 1 2 3 4 5 And B 0 3 6 Find A B 0 6 3 Chegg Find a – b and b – a. a – b = a – (a ∩ b) a ∩ b = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} ∩ {2, 4, 6, 8} = {2, 4, 6} a – b = a – (a ∩ b) = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} – {2, 4, 6} = {1, 3, 5} b – a = b – (b ∩ a) = b – (a ∩ b) = {2,. To solve the problem step by step, we will follow the instructions given in the question. the intersection a′∩b′ consists of elements that are common to both a′ and b′. the union a∪b consists of all elements that are in either a or b or in both. the complement of a∪b is defined as the universal set u minus the elements of a∪b. There are 2 steps to solve this one. in set theory, the operations you're trying to perform involve two sets, a and b. let's work t let a={1,2,3,4,5} and b= {0,3,6}. find. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. answer to let a= {1,2,3,4,5} and b= {0,3,6}. find. Let a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and b = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. then the number of functions f : a → b satisfying f (1) f (2) = f (4) – 1 is equal to. When given the sets a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and b = {0, 3, 6}, the operations yield the following results: a) a∪b = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, b) a∩b = {3}, c) a−b = {1, 2, 4, 5}, and d) b−a = {0, 6}. The union of the sets a a a and b b b, denoted by a ∪ b a \cup b a∪ b, is the set that contains those elements that are either in a a a or in b b b, or in both. find step by step discrete maths solutions and the answer to the textbook question let a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and b = {0, 3, 6}. find a) a ∪ b. b) a ∩ b. c) a − b. d) b − a.

8 Let A 1 2 3 4 5 B 3 4 5 6 7 And C Chegg There are 2 steps to solve this one. in set theory, the operations you're trying to perform involve two sets, a and b. let's work t let a={1,2,3,4,5} and b= {0,3,6}. find. not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. answer to let a= {1,2,3,4,5} and b= {0,3,6}. find. Let a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and b = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. then the number of functions f : a → b satisfying f (1) f (2) = f (4) – 1 is equal to. When given the sets a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and b = {0, 3, 6}, the operations yield the following results: a) a∪b = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, b) a∩b = {3}, c) a−b = {1, 2, 4, 5}, and d) b−a = {0, 6}. The union of the sets a a a and b b b, denoted by a ∪ b a \cup b a∪ b, is the set that contains those elements that are either in a a a or in b b b, or in both. find step by step discrete maths solutions and the answer to the textbook question let a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and b = {0, 3, 6}. find a) a ∪ b. b) a ∩ b. c) a − b. d) b − a.
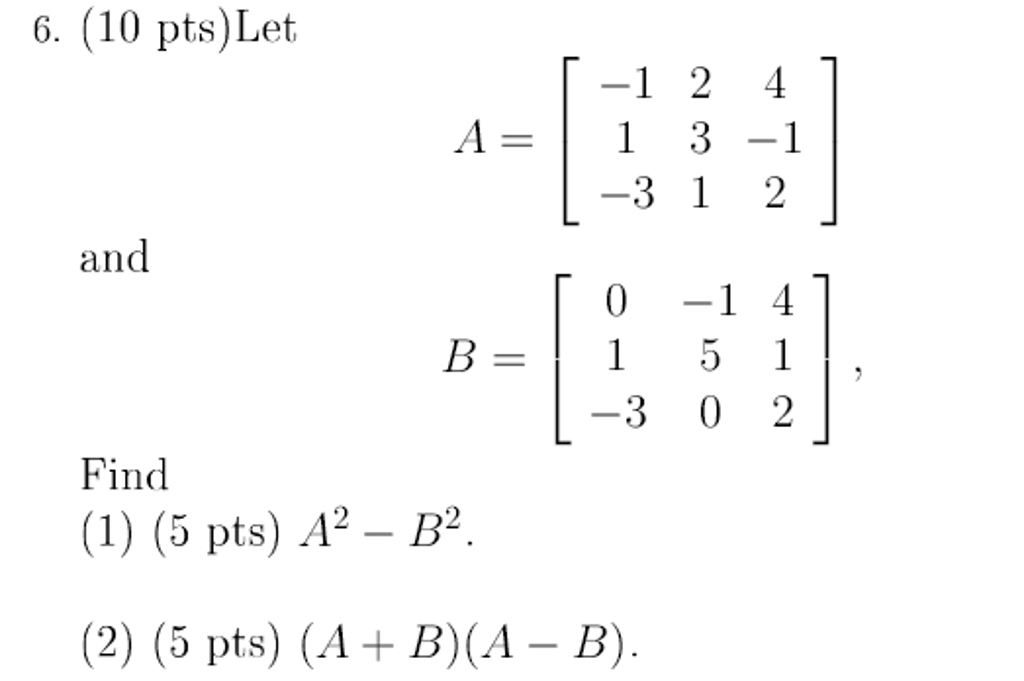
Solved Let A 1 1 3 2 3 1 4 1 2 And B 0 1 3 1 Chegg When given the sets a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and b = {0, 3, 6}, the operations yield the following results: a) a∪b = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, b) a∩b = {3}, c) a−b = {1, 2, 4, 5}, and d) b−a = {0, 6}. The union of the sets a a a and b b b, denoted by a ∪ b a \cup b a∪ b, is the set that contains those elements that are either in a a a or in b b b, or in both. find step by step discrete maths solutions and the answer to the textbook question let a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and b = {0, 3, 6}. find a) a ∪ b. b) a ∩ b. c) a − b. d) b − a.

Solved Let U 1 2 3 4 5 6 A 1 2 4 And B 3 4 5 6 Write Chegg
Comments are closed.