Solved Example 3 I Find The Domain Of The Bessel Function Of Chegg

Solved Example 3 Find The Domain Of The Bessel Function Of Chegg There are 2 steps to solve this one. example 3 find the domain of the bessel function of order 0 defined by j. (x) = ( 1 x2n 22n (n!) solution dn 11 an let an = ( 1)"x21 [22n (n!)?]. then ( 1) 1x2 (n 1) 22n (n!)2 ( 1)"x2n x2n 2 22n (n!)² 22n 2 (n 1)2 (n!)2 x2n <1 for all x. To find the domain of the bessel function of order 0, we are given the series: j 0(x) = n=0∑∞ 22n(n!)2(−1)nx2n. to determine the domain, we need to establish for which values of x this series converges. we use the ratio test for this purpose. the general term in the series is: an = 22n(n!)2(−1)nx2n. for the ratio test, we calculate:.

Solved Example 3 Find The Domain Of The Bessel Function Of Chegg Example: suppose the potential is ρ v (ρ) = v0 a sin on a plane at ρ a z = 0, and we want to find the potential for z > 0. then the appropriate function of z is e−kz, chosen so that Φ → 0 as z → ∞ ( a long way from the plane). To satisfy the boundary conditions (3), (4), we plug z = 0 or z = h and use fourier bessel formulas. which is formula (29) in the handout \bessel functions". The function in brackets is known as the bessel function of the first kind of order zero and is denoted by j 0(x). it follows from theorem 5.7.1 that the series converges for all x, and that j. Solution of equation (1) when α = n. consider α = n ε 6∈z corresponding bessel equation has two independent solutions jn ε and j (n ε). − the function yn ε defined by jn ε(x) ( 1)nj (n ε)(x) yn ε(x) = − − − . ε since function yn ε is a linear combination of jn ε and solution of the corresponding bessel’s equation of order.
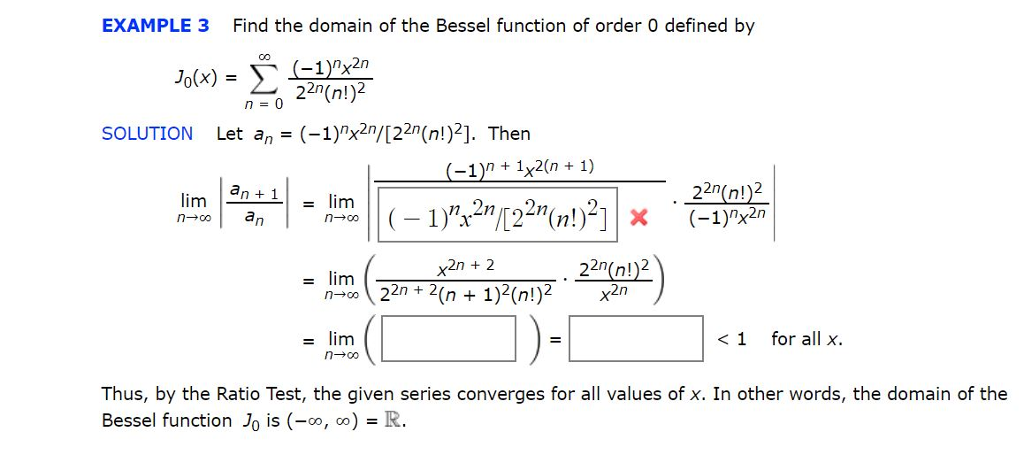
Solved Example 3 Find The Domain Of The Bessel Function Of Chegg The function in brackets is known as the bessel function of the first kind of order zero and is denoted by j 0(x). it follows from theorem 5.7.1 that the series converges for all x, and that j. Solution of equation (1) when α = n. consider α = n ε 6∈z corresponding bessel equation has two independent solutions jn ε and j (n ε). − the function yn ε defined by jn ε(x) ( 1)nj (n ε)(x) yn ε(x) = − − − . ε since function yn ε is a linear combination of jn ε and solution of the corresponding bessel’s equation of order. This bessel function calculator will solve for bessel functions of the first, second, and third kind simultaneously. all you need to input are the order ν ν and x x, the point at which you desire to evaluate. The function ym(x) is called a bessel function of the 2nd kind of order m; or a neumann function, or a weber function. the functions y0(x); y1(x); and y2(x) are plotted below. Plots of the bessel functions j0(x),j1(x),j2(x) j 0 (x), j 1 (x), j 2 (x), and j3(x) j 3 (x). a second linearly independent solution is obtained for p p not an integer as j−p(x) j − p (x). The integral representation is; π π jn(x) = (1 π) r0 dω cos(x sin(ω) − nω) = (1 2π) dω ei(xsin(ω)−nω) this implies that the bessel function, jn, is the nth fourier coefficient of the expansion; ∞ ei2sin(ω) = jneinω. the following expressions for the generating function are obtained. n=−∞ p.
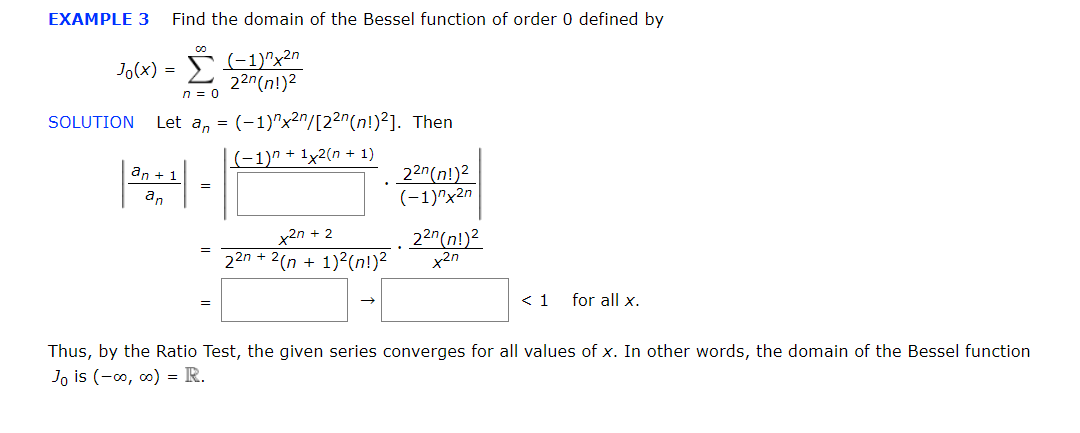
Solved Example 3 Find The Domain Of The Bessel Function Of Chegg This bessel function calculator will solve for bessel functions of the first, second, and third kind simultaneously. all you need to input are the order ν ν and x x, the point at which you desire to evaluate. The function ym(x) is called a bessel function of the 2nd kind of order m; or a neumann function, or a weber function. the functions y0(x); y1(x); and y2(x) are plotted below. Plots of the bessel functions j0(x),j1(x),j2(x) j 0 (x), j 1 (x), j 2 (x), and j3(x) j 3 (x). a second linearly independent solution is obtained for p p not an integer as j−p(x) j − p (x). The integral representation is; π π jn(x) = (1 π) r0 dω cos(x sin(ω) − nω) = (1 2π) dω ei(xsin(ω)−nω) this implies that the bessel function, jn, is the nth fourier coefficient of the expansion; ∞ ei2sin(ω) = jneinω. the following expressions for the generating function are obtained. n=−∞ p.
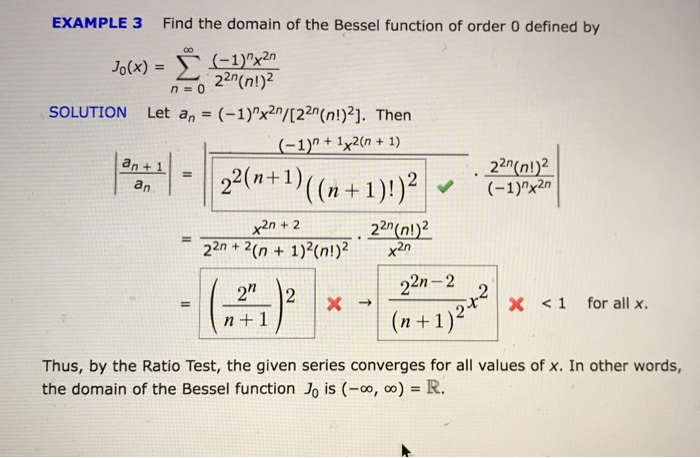
Solved Example 3 Find The Domain Of The Bessel Function Of Chegg Plots of the bessel functions j0(x),j1(x),j2(x) j 0 (x), j 1 (x), j 2 (x), and j3(x) j 3 (x). a second linearly independent solution is obtained for p p not an integer as j−p(x) j − p (x). The integral representation is; π π jn(x) = (1 π) r0 dω cos(x sin(ω) − nω) = (1 2π) dω ei(xsin(ω)−nω) this implies that the bessel function, jn, is the nth fourier coefficient of the expansion; ∞ ei2sin(ω) = jneinω. the following expressions for the generating function are obtained. n=−∞ p.
Comments are closed.