Solved Computer Org Architecture Class All 1 Assignment Chegg
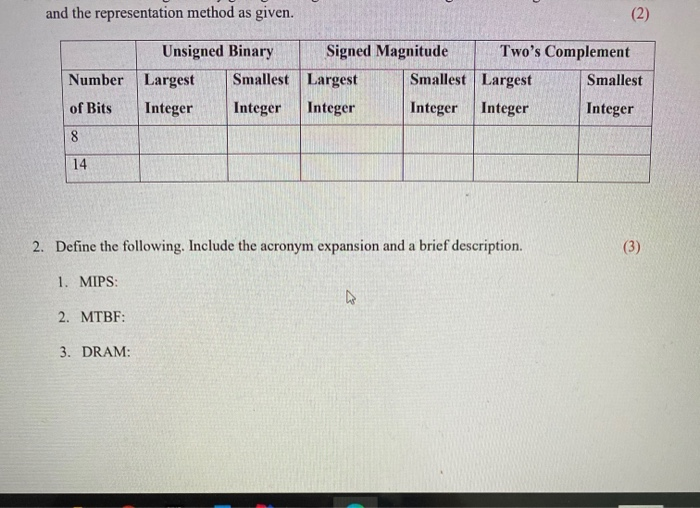
Solved Assignment 1 Syst26671 Computer Architecture Chegg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. there’s just one step to solve this. $12: 0x. Our resource for computer organization and architecture includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step.
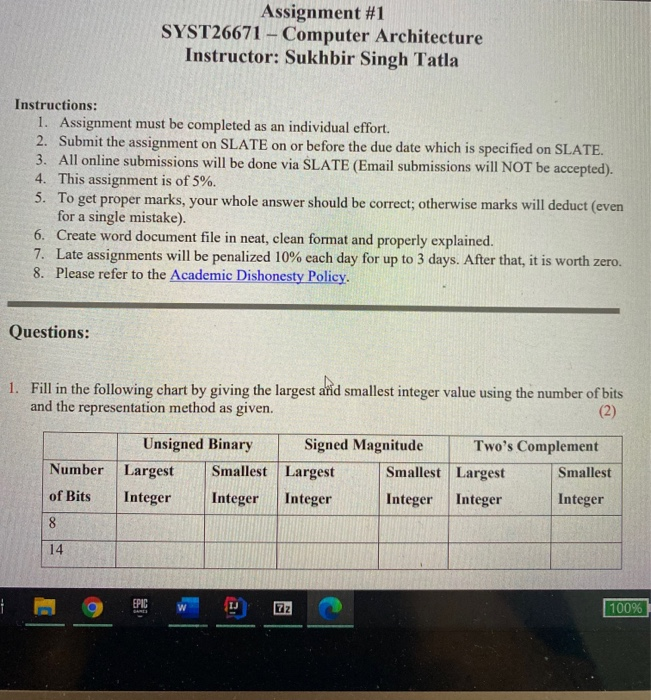
Solved Assignment 1 Syst26671 Computer Architecture Chegg This document contains an assignment submitted by diego jay g. vasquez for a computer system architecture course. the assignment includes: 1) answers to review questions from chapter 9 of the textbook "computer organization and architecture" by william stallings. Selected solutions to problem set #1 coe608: computer organization and architecture introduction, instruction set architecture and computer arithmetic chapters 1, 2 and 3 a. chapter 1: exercises: 1.1.1 => 1.1.26 1.1.1 computer used to run large problems and usually accessed via a network: 5 supercomputers 1.1.2 1015 or 250 bytes: 7 petabyte. Material type: assignment; class: computer org i; subject: computer design architecture; university: florida state university; term: spring 2001;. To differentiate between computer architecture and computer organization, focus on explaining how computer organization deals with the connection and physical aspects of hardware components in a system, whereas computer architecture deals with the logical aspects such as the instruction set and system behavior visible to the user.

Solved Computer Org Architecture Class All 1 Assignment Chegg Material type: assignment; class: computer org i; subject: computer design architecture; university: florida state university; term: spring 2001;. To differentiate between computer architecture and computer organization, focus on explaining how computer organization deals with the connection and physical aspects of hardware components in a system, whereas computer architecture deals with the logical aspects such as the instruction set and system behavior visible to the user. (problem 1) consider two different implementations of the same instruction set architecture. the instructions can be divided into four classes according to their cpi (class a, b, c, and d). This document contains an assignment for a computer architecture course. it includes 5 questions about various topics in computer architecture: 1) it distinguishes between programmed i o and interrupt driven i o, and explains how each affects performance. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: assignment #1 problem # 1: what is the main difference between computer architecture and computer organization by giving examples of each that differ from those mentioned in the course slides?. General purpose registers are used to store temporary data within the microprocessor. there are 8 general purpose registers in 8086 microprocessor. ax – this is the accumulator. it is of 16 bits and is divided into two 8 bit registers ah and al to also perform 8 bit instructions.
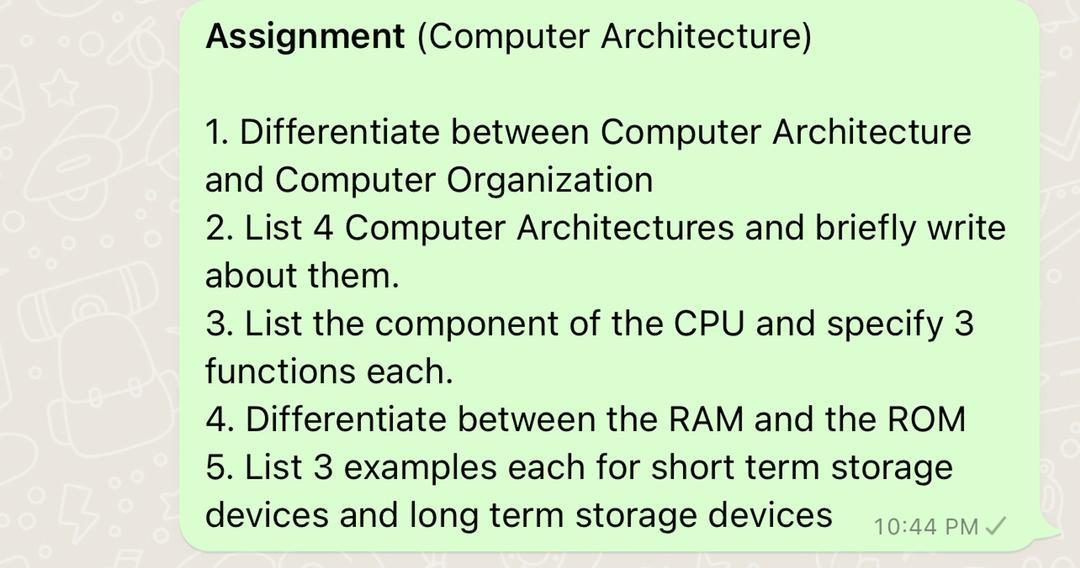
Solved Assignment Computer Architecture 1 Differentiate Chegg (problem 1) consider two different implementations of the same instruction set architecture. the instructions can be divided into four classes according to their cpi (class a, b, c, and d). This document contains an assignment for a computer architecture course. it includes 5 questions about various topics in computer architecture: 1) it distinguishes between programmed i o and interrupt driven i o, and explains how each affects performance. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: assignment #1 problem # 1: what is the main difference between computer architecture and computer organization by giving examples of each that differ from those mentioned in the course slides?. General purpose registers are used to store temporary data within the microprocessor. there are 8 general purpose registers in 8086 microprocessor. ax – this is the accumulator. it is of 16 bits and is divided into two 8 bit registers ah and al to also perform 8 bit instructions.
Comments are closed.