Solved Coalescent Theory Predicts That Most Coalescent Chegg

Solved Coalescent Theory Predicts That Most Coalescent Chegg There are 3 steps to solve this one. genetics: the study of heredity, particularly how genes interact with one another and with variation not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. Coalescent theory is a fundamental concept in population genetics that traces the ancestral lineage of gene copies within a population back to a common ancestor. developed in the 1980s by john kingman, this mathematical framework models how genetic variation emerges and is shaped over generations.

Solved Coalescent Theory Predicts That Most Coalescent Chegg The sample genealogies central to this approach can be conveniently modeled using a continuous time markov process known as the coalescent (or kingman's coalescent, or sometimes“the n coalescent” to emphasize the depen dence on the sample size). Based on a sample of extant gene copies and equipped with our favourite model of evolution, we use the coalescent to estimate population genetic parameters associated with coalescent events i.e. when was the most recent common ancestor of existing gene copies? what was the population size at the time of the coalescent event?. We can recall the results of neutral coalescent theory, that the average time back to the common ancestor for a sample of size n = 2 is equal to 1 (i.e. 2n generations) and the average time to the most recent common ancestor of all members of a large sample is ~2 (i.e. ~4n generations). Introduction to coalescent theory the wright fisher population model serially sampled sequences and population size change estimating effective population size, with examples population subdivision and incomplete lineage sorting. access easy to understand explanations and practical examples on key biology topics, from cells to ecosystems.

Solved How Might Coalescent Theory Assist Conservation Chegg We can recall the results of neutral coalescent theory, that the average time back to the common ancestor for a sample of size n = 2 is equal to 1 (i.e. 2n generations) and the average time to the most recent common ancestor of all members of a large sample is ~2 (i.e. ~4n generations). Introduction to coalescent theory the wright fisher population model serially sampled sequences and population size change estimating effective population size, with examples population subdivision and incomplete lineage sorting. access easy to understand explanations and practical examples on key biology topics, from cells to ecosystems. Coalescent theory describes the ancestral relationships (i.e. genealogy) of idealized individuals sampled from a larger population. we envision these sampled lineages are embedded within the full ancestral history of the population. such that individuals leave a random number of offspring. Here’s the best way to solve it. introduction: population genetics is defined as the study involving variations in genes within a population. this process involves the analysis to check the changes in the frequencies of alleles within populations for a time period. in genetics genes … not the question you’re looking for?. The (continous) coalescent and the wright fisher population model the coalescent process is in effect a sequence of n−1 poisson processes1, with rates rk= k(k −1) 2 ,k= n,n−1,n−2, ,2 describing the poisson process at which two of the equivalence classes merge when there are k equivalence classes. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like coalescent theory, coalescence, probability of coalescence in each generation and more.
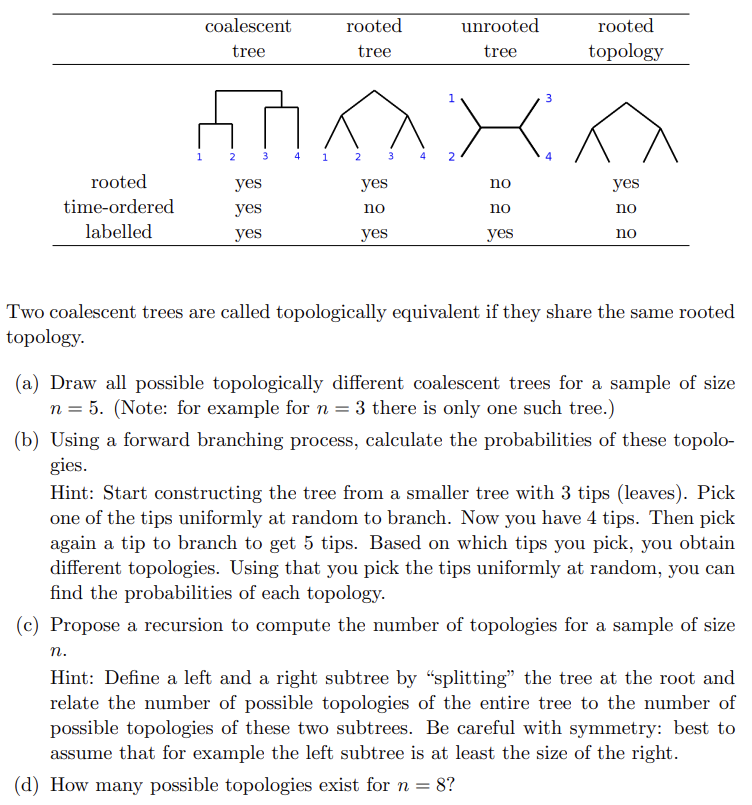
Solved Topologies Of Coalescent Trees We Use The Following Chegg Coalescent theory describes the ancestral relationships (i.e. genealogy) of idealized individuals sampled from a larger population. we envision these sampled lineages are embedded within the full ancestral history of the population. such that individuals leave a random number of offspring. Here’s the best way to solve it. introduction: population genetics is defined as the study involving variations in genes within a population. this process involves the analysis to check the changes in the frequencies of alleles within populations for a time period. in genetics genes … not the question you’re looking for?. The (continous) coalescent and the wright fisher population model the coalescent process is in effect a sequence of n−1 poisson processes1, with rates rk= k(k −1) 2 ,k= n,n−1,n−2, ,2 describing the poisson process at which two of the equivalence classes merge when there are k equivalence classes. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like coalescent theory, coalescence, probability of coalescence in each generation and more.
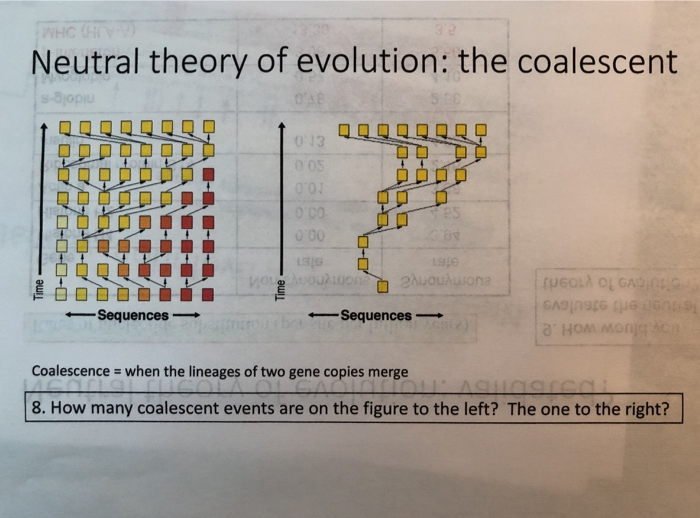
Solved Neutral Theory Of Evolution The Coalescent 045 13 Es Chegg The (continous) coalescent and the wright fisher population model the coalescent process is in effect a sequence of n−1 poisson processes1, with rates rk= k(k −1) 2 ,k= n,n−1,n−2, ,2 describing the poisson process at which two of the equivalence classes merge when there are k equivalence classes. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like coalescent theory, coalescence, probability of coalescence in each generation and more.

Coalescent Theory Kevin R Thornton Observable
Comments are closed.