Reverse Transcriptases Used In Rt Pcr

A Concise Guide To Reverse Transcriptase Pcr Rt Pcr Principles Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rt pcr) is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of rna into dna (in this context called complementary dna or cdna) and amplification of specific dna targets using polymerase chain reaction (pcr). [1]. In two step rt pcr, 3 types of primers, and mixtures thereof, can be used for reverse transcription: oligo dt primers (typically 13–18mers), random oligomers (such as hexamers, octamers, or nonamers), or gene specific primers (see table “suitability of primer types for rt pcr”).
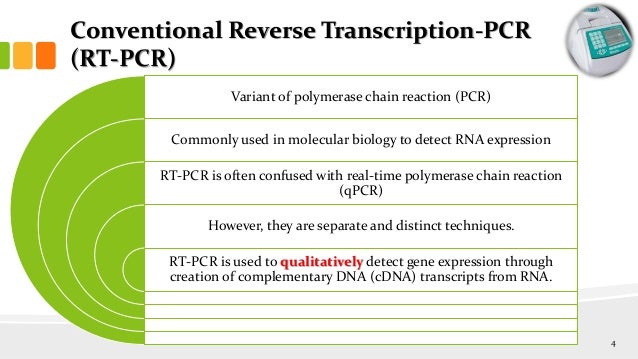
Rt Pcr Reverse Transcription Pcr Reverse transcriptase pcr (rt pcr) is a variation of the polymerase chain reaction that amplifies target rna. addition of reverse transcriptase (rt) enzyme prior to pcr makes it possible to amplify and detect rna targets. Rt pcr (reverse transcription pcr) approaches are used among others to detect expression levels of particular genes,[11] to generate cdna libraries,[12] to identify rna levels in patient samples for clinical diagnostic[13] or in newly developed next generation rna sequencing technologies.[14]. Reverse transcriptases (rts) use an rna template and a short primer complementary to the 3 end of the rna to direct the synthesis of the first strand cdna, which can be used directly as a template for applications such as pcr, qpcr, lamp, or sequencing workflows. An rt pcr reaction requires several key components: the rna template to be analyzed, reverse transcriptase to convert rna into complementary dna (cdna), and primers (such as oligo (dt) or gene specific primers) to initiate both reverse transcription and pcr amplification.

Reverse Transcription Pcr Rt Pcr Aat Bioquest Reverse transcriptases (rts) use an rna template and a short primer complementary to the 3 end of the rna to direct the synthesis of the first strand cdna, which can be used directly as a template for applications such as pcr, qpcr, lamp, or sequencing workflows. An rt pcr reaction requires several key components: the rna template to be analyzed, reverse transcriptase to convert rna into complementary dna (cdna), and primers (such as oligo (dt) or gene specific primers) to initiate both reverse transcription and pcr amplification. Reverse transcription: next, rna is converted into complementary dna (cdna) using a reverse transcriptase. these enzymes are naturally found in retroviruses such as hiv, where they convert the rna genome into dna to integrate into the host genome for replication. Reverse transcription combined with pcr, or reverse transcription pcr (rt pcr), allows detection of rna even at very low levels of gene expression and paves the way for detection of circulating rna, rna viruses, and cancerous gene fusions in molecular diagnostics [11–13]. The method uses an enzyme called reverse transcriptase (proper name is rna dependent dna polymerase) to synthesize a complementary strand of dna (complementary dna, or cdna) from an rna template. the resulting cdna is then used as template in a pcr assay using dna polymerase. Reverse transcriptases (rts) are enzymes that can generate a complementary strand of dna (cdna) from rna. coupled with pcr, rts have been widely used to detect rnas and to clone expressed genes. classical retroviral rts have been improved by protein engineering.

Reverse Transcription Pcr Rt Pcr Aat Bioquest Reverse transcription: next, rna is converted into complementary dna (cdna) using a reverse transcriptase. these enzymes are naturally found in retroviruses such as hiv, where they convert the rna genome into dna to integrate into the host genome for replication. Reverse transcription combined with pcr, or reverse transcription pcr (rt pcr), allows detection of rna even at very low levels of gene expression and paves the way for detection of circulating rna, rna viruses, and cancerous gene fusions in molecular diagnostics [11–13]. The method uses an enzyme called reverse transcriptase (proper name is rna dependent dna polymerase) to synthesize a complementary strand of dna (complementary dna, or cdna) from an rna template. the resulting cdna is then used as template in a pcr assay using dna polymerase. Reverse transcriptases (rts) are enzymes that can generate a complementary strand of dna (cdna) from rna. coupled with pcr, rts have been widely used to detect rnas and to clone expressed genes. classical retroviral rts have been improved by protein engineering.

Reverse Transcriptase Rt Pcr Download Table The method uses an enzyme called reverse transcriptase (proper name is rna dependent dna polymerase) to synthesize a complementary strand of dna (complementary dna, or cdna) from an rna template. the resulting cdna is then used as template in a pcr assay using dna polymerase. Reverse transcriptases (rts) are enzymes that can generate a complementary strand of dna (cdna) from rna. coupled with pcr, rts have been widely used to detect rnas and to clone expressed genes. classical retroviral rts have been improved by protein engineering.

Reverse Transcription Pcr Rt Pcr Purpose Types Procedure Result
Comments are closed.