Read Only Memory Rom Tutorial Circuits Microprocessor System
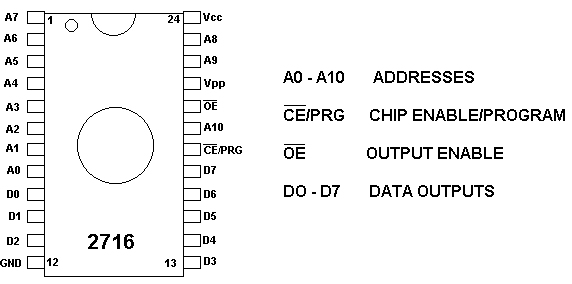
Read Only Memory Rom Tutorial Circuits Microprocessor System Memory plays a crucial role in how devices operate, and one of the most important types is read only memory (rom). unlike ram (random access memory), which loses its data when the power is turned off, rom is designed to store essential information permanently. Memory chips are simply a collection of registers, each with its own address. data, in the form of 0's and 1's, is stored in the registers. rom chips can be read from, but not written to. they are non volatile, which means that they retain their contents after power is removed. most roms are programmed during manufacture of the chips.
Read Only Memory Rom In programmable read only memory (prom), the data can be stored after the manufacturing process or in the field. the method of programming as well as the number of times it can be programmed gives way to a number of subtypes. one time programmable (otp) rom can only be programmed once. In this tutorial, you will explore the fundamentals of read only memory (rom), including its definition, types, architecture, features, and characteristics. you will also learn how to calculate output and address lines in rom and examine its applications across various fields, highlighting its significance in electronic devices and systems. As the name implies, a read only memory (rom) is a memory unit that performs the read operation only; it does not have a write capability. this implies that the binary information stored in a rom is made permanent during the hardware production of the unit and cannot be altered by writing different words into it. Read only memory (rom): a read only memory (rom) is a device that includes both the decoder and the or gates within a single ic package. the fig. 3.82 shows the block diagram of rom. it consists of n input lines and m output lines. each bit combination of the input variables is called an address.

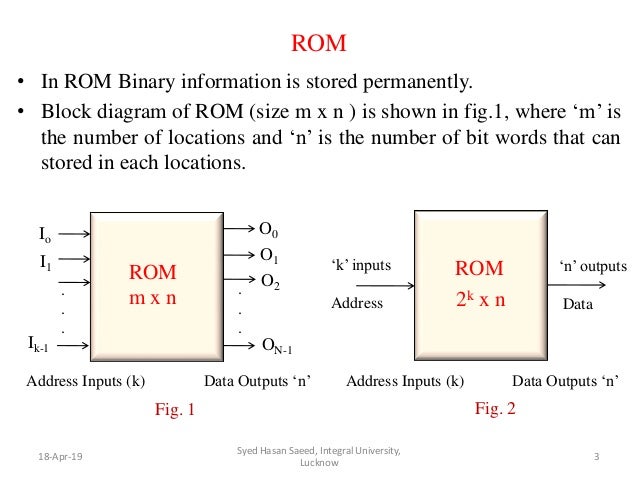
Read Only Memory Digital Circuits 5 Memories Adafruit Learning System As the name implies, a read only memory (rom) is a memory unit that performs the read operation only; it does not have a write capability. this implies that the binary information stored in a rom is made permanent during the hardware production of the unit and cannot be altered by writing different words into it. Read only memory (rom): a read only memory (rom) is a device that includes both the decoder and the or gates within a single ic package. the fig. 3.82 shows the block diagram of rom. it consists of n input lines and m output lines. each bit combination of the input variables is called an address. Digital electronics | read only memory (rom): in this tutorial, we will learn about read only memory (rom) in detail, what is the usage of rom, their design procedure, and the different types of rom. Read only memory (rom) is similar in design to static or dynamic ram circuits, except that the “latching” mechanism is made for one time (or limited) operation. the simplest type of rom is that which uses tiny “fuses” which can be selectively blown or left alone to represent the two binary states. Rom operates using a combination of hardware and logical components to store and retrieve data efficiently. the rom block diagram illustrates how data flows within the system: inputs: k input lines specify an address. outputs: n output lines deliver the stored data. Read only memory devices are a special case of memory where, in normal system operation, the memory is read but not changed. read only memories are non volatile, that is, stored informa tion is retained when the power is removed. the main read only memory devices are listed below:.

Creative Rom Read Only Memory Digital electronics | read only memory (rom): in this tutorial, we will learn about read only memory (rom) in detail, what is the usage of rom, their design procedure, and the different types of rom. Read only memory (rom) is similar in design to static or dynamic ram circuits, except that the “latching” mechanism is made for one time (or limited) operation. the simplest type of rom is that which uses tiny “fuses” which can be selectively blown or left alone to represent the two binary states. Rom operates using a combination of hardware and logical components to store and retrieve data efficiently. the rom block diagram illustrates how data flows within the system: inputs: k input lines specify an address. outputs: n output lines deliver the stored data. Read only memory devices are a special case of memory where, in normal system operation, the memory is read but not changed. read only memories are non volatile, that is, stored informa tion is retained when the power is removed. the main read only memory devices are listed below:.
Read Only Memory Rom Rom operates using a combination of hardware and logical components to store and retrieve data efficiently. the rom block diagram illustrates how data flows within the system: inputs: k input lines specify an address. outputs: n output lines deliver the stored data. Read only memory devices are a special case of memory where, in normal system operation, the memory is read but not changed. read only memories are non volatile, that is, stored informa tion is retained when the power is removed. the main read only memory devices are listed below:.

Read Only Memory Rom Working Types Applications Advantages
Comments are closed.