Phase Diagram And Cooling Curve Pdf

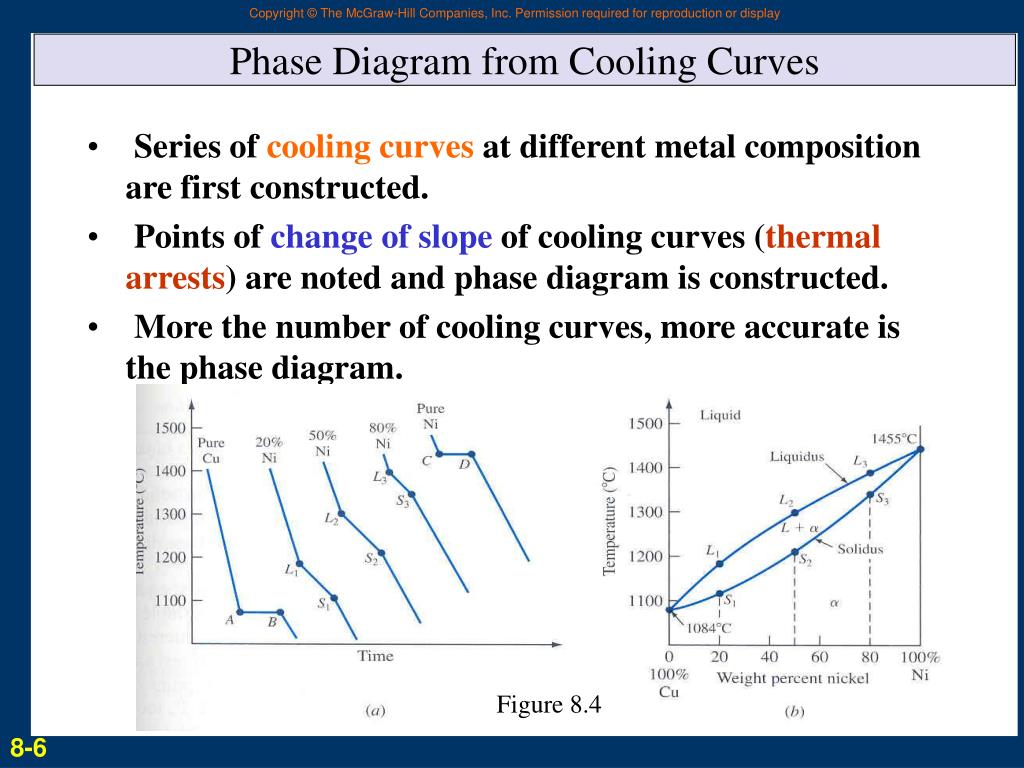
Heating And Cooling Curves вђ Overview Examples Expii Phase diagram and “degrees of freedom”. phase diagrams is a type of graph used to show the equilibrium conditions between the thermodynamically distinct phases; or to show what phases are present in the material system at various t, p, and compositions. “equilibrium” is important: phase diagrams are determined by using slow cooling. By removing the time axis from the curves and replacing it with composition, the cooling curves indicate the temperatures of the solidus and liquidus for a given composition. this allows the solidus and liquidus to be plotted to produce the phase diagram: this page titled 12.5: interpretation of cooling curves is shared under a cc by nc sa.

Phase Diagram Heating And Cooling Curves Phase Matter Chemistry A cooling curve for a sample that begins at the temperature and composition given by point a is shown in figure 8.10.1b 8.10. 1 b. figure 8.10.1 8.10. 1: (a) cooling of a two component system from liquid to solid. (b) cooresponding cooling curve for this process. as the sample cools from point a, the temperature will decrease at a rate. Wα wl = 1. mass of a component that is present in both phases equal to the mass of the component in one phase mass of the component in the second phase: wαcα wlcl = co. solution of these equations gives us the lever rule. wl = (cα co) (cα cl) wα = (co cl) (cα cl) phase compositions and amounts. The most common approaches for the determination of phase diagram of two component systems are “cooling curve” and “thaw melt” methods. these methods are quite popular due to their easiness and practicability to many systems. 1. cooling curve method: in this approach, a liquid mixture of two components a and b at temperature t is. In order to plot out a phase diagram, we need to be able to see how temperature affects these curves. and we need to know whether or not these curves imply phase separation. finally we need to know, if phase separation occurs, how much of each phase is present. lever rule for determining proportions of phases.

Heating And Cooling Curves Explained The most common approaches for the determination of phase diagram of two component systems are “cooling curve” and “thaw melt” methods. these methods are quite popular due to their easiness and practicability to many systems. 1. cooling curve method: in this approach, a liquid mixture of two components a and b at temperature t is. In order to plot out a phase diagram, we need to be able to see how temperature affects these curves. and we need to know whether or not these curves imply phase separation. finally we need to know, if phase separation occurs, how much of each phase is present. lever rule for determining proportions of phases. Cooling curves are shown on the temperature log time plot. at the end of the cooling curve phases are shown at room temperature. variation in hardness with distance from jominy end is also shown in the diagram. for cooling curve b, at t 1 temperature minimum t 1 timing is required to nucleate pearlite as per ttt diagram in fig. 8. but material. Equilibrium phase diagrams are one of the single most useful tools of a materials scientist and engineer. as maps of the temperature ranges and solubility limits of each known phase in the alloy system, including compounds, they are obviously useful to metal casters, heat treaters and ceramicists and are an invaluable tool in alloy design, in.
Cooling Curve Phase Diagram Cooling curves are shown on the temperature log time plot. at the end of the cooling curve phases are shown at room temperature. variation in hardness with distance from jominy end is also shown in the diagram. for cooling curve b, at t 1 temperature minimum t 1 timing is required to nucleate pearlite as per ttt diagram in fig. 8. but material. Equilibrium phase diagrams are one of the single most useful tools of a materials scientist and engineer. as maps of the temperature ranges and solubility limits of each known phase in the alloy system, including compounds, they are obviously useful to metal casters, heat treaters and ceramicists and are an invaluable tool in alloy design, in.

Cooling Curve Spm Chemistry

Comments are closed.