Ofdm Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing

Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing Ofdm Topic Knowledgepicker In telecommunications, orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (ofdm) is a type of digital transmission used in digital modulation for encoding digital (binary) data on multiple carrier frequencies. Ofdm is similar to the broadcasting technique known as frequency division multiplexing (also known as fdm), which uses a multitude of transmitters and receivers to send information on different frequencies over a single wire, such as an electrical power cable.

Pdf Pcc Ofdm Enhancing Frequency Sensitivity Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (ofdm) is a method of data transmission where a single information stream is split among several closely spaced narrowband subchannel frequencies instead of a single wideband channel frequency. Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (ofdm) is a digital multi carrier modulation scheme that extends the concept of single subcarrier modulation by using multiple subcarriers within the same single channel. Abstract orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (ofdm) is a multi carrier modulation scheme that provides efficient bandwidth utilization and robustness against time dispersive channels. this paper deals with the basic system model for ofdm based systems and with self interference, or the corruption of desired signal by itself in ofdm systems. Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (ofdm) is an efficient modulation format used in modern wireless communication systems including 5g. ofdm combines the benefits of quadrature amplitude modulation (qam) and frequency division multiplexing (fdm) to produce a high data rate communication system.
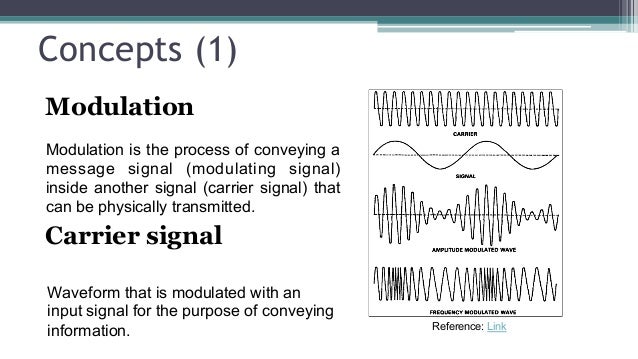
Ofdm Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing Abstract orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (ofdm) is a multi carrier modulation scheme that provides efficient bandwidth utilization and robustness against time dispersive channels. this paper deals with the basic system model for ofdm based systems and with self interference, or the corruption of desired signal by itself in ofdm systems. Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (ofdm) is an efficient modulation format used in modern wireless communication systems including 5g. ofdm combines the benefits of quadrature amplitude modulation (qam) and frequency division multiplexing (fdm) to produce a high data rate communication system. The perplexing and bursty phenomenon known as orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (ofdm) is a multi carrier modulation technique that utilizes subcarriers packed closely together to transmit data. Ofdma: orthogonal frequency division multiple access. a scheme used to provide a multiple access capability for applications such as cellular telecommunications when using ofdm technologies. Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (ofdm) is a widely used modulation scheme that forms the basis of 4g 5g mobile communications systems. in the wideband multicarrier scheme, information symbols are multiplexed on closely spaced orthogonal subcarriers. Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing, or ofdm, is a method used to transmit large amounts of data over a radio wave. it does this by dividing the signal into several narrower bands, each transmitted on its own frequency.
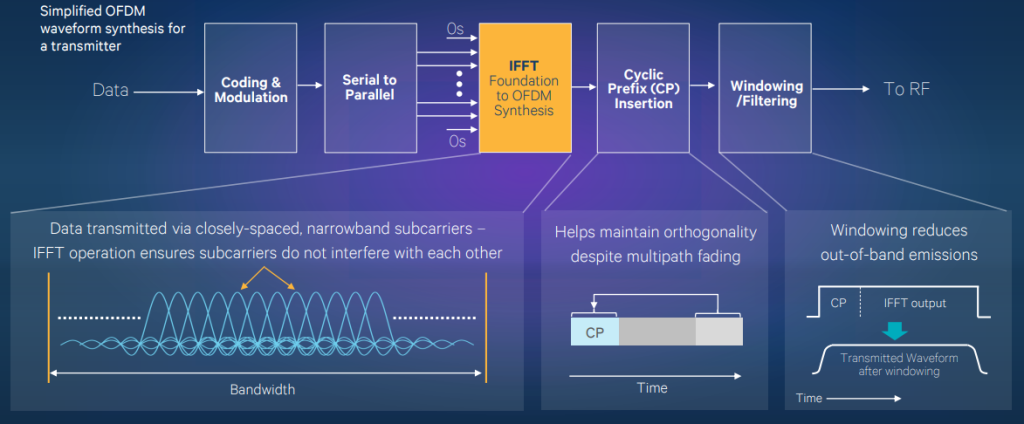
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing Ofdm Rf Engineer Network The perplexing and bursty phenomenon known as orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (ofdm) is a multi carrier modulation technique that utilizes subcarriers packed closely together to transmit data. Ofdma: orthogonal frequency division multiple access. a scheme used to provide a multiple access capability for applications such as cellular telecommunications when using ofdm technologies. Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (ofdm) is a widely used modulation scheme that forms the basis of 4g 5g mobile communications systems. in the wideband multicarrier scheme, information symbols are multiplexed on closely spaced orthogonal subcarriers. Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing, or ofdm, is a method used to transmit large amounts of data over a radio wave. it does this by dividing the signal into several narrower bands, each transmitted on its own frequency.
Comments are closed.