Mnemonic For Jones Criteria For Rheumatic Fever Diagnosis Jones Criteria Major And Minor Mnemonic

Medical Mnemonics Major And Minor Criteria For Rheumatic Fever U Rheumatic fever occurs after a streptococcal infection (usually caused by group a beta hemolytic strep (gabhs)). it is an inflammatory condition that affects the joints, skin, heart and brain. major criteria are referred to as jones criteria and can be remembered by the mnemonic of the same name. Share this post. “rheumatic fever (rf) is an inflammatory disease that can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain. the disease typically develops two to four weeks after a streptococcal throat infection.”. duckett jones diagnostic criteria: “the revised jones criteria are guidelines decided on by the american heart association to help.
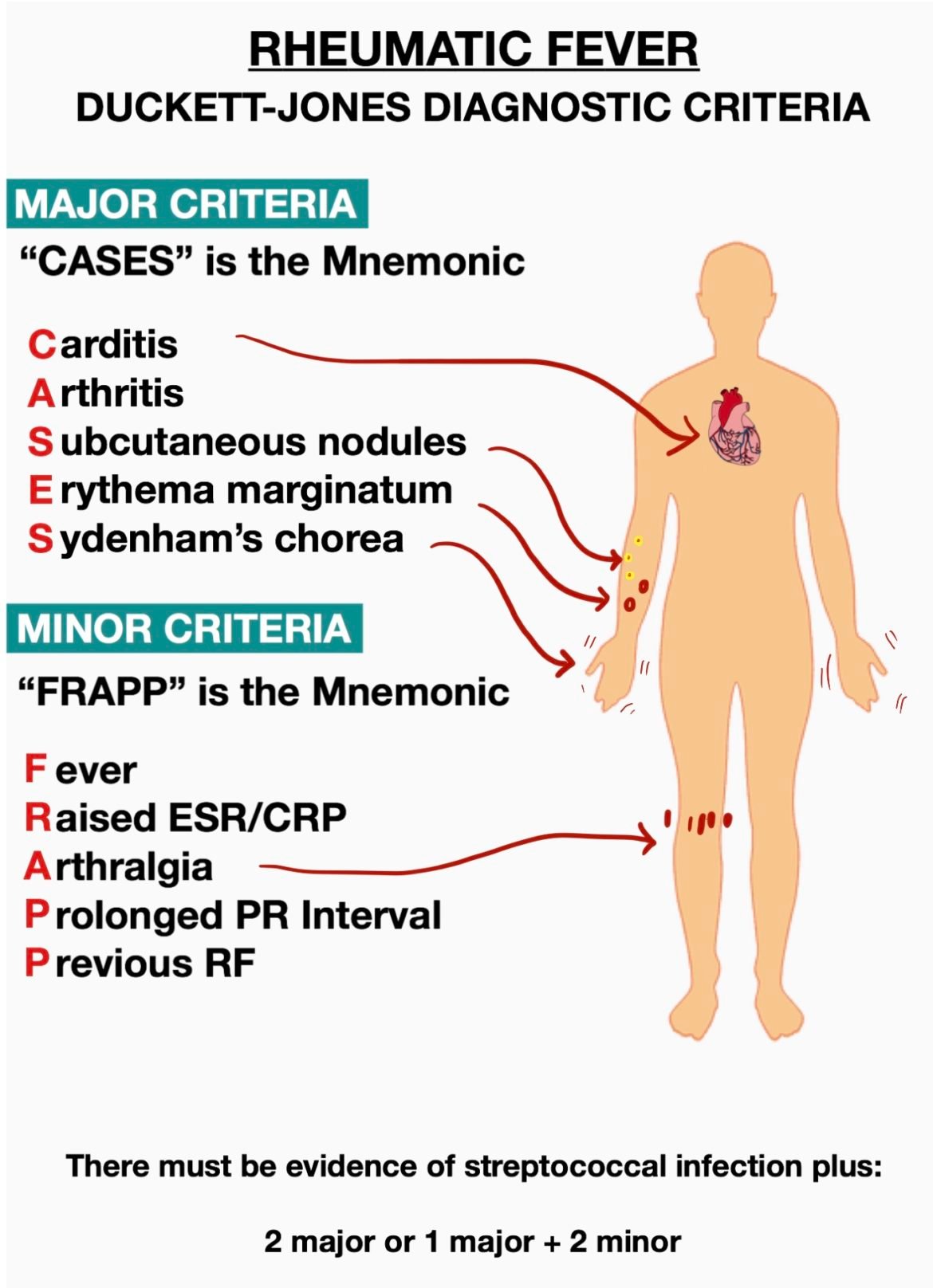
Rheumatic Fever Diagnostic Criteria Mnemonics Medical Junction Minor criteria: olyarthralgia, fever (≥38.5° f), sedimentation rate ≥60 mm and or c reactive protein (crp) ≥3.0 mg dl, and prolonged pr interval (unless carditis is a major criterion) revised jones criteria, moderate and high risk populations: major and minor criteria are as follows: major criteria: carditis (clinical and or subclinical. Jones criteria, 1992 update. special writing group of the committee on rheumatic fever, endocarditis, and kawasaki disease of the council on cardiovascular disease in the young of the american heart association. jama. 1992;268 (15):2069 73. this jones criteria calculator diagnoses acute rheumatic fever based on presence of major and minor. Rheumatic fever was fairly common in the uk up until the 1960s, but is, thankfully, now rare in the developed world, with current uk incidence reported as less than 1 in 100,000. 1. this is largely due to major public health interventions, including the more widespread use of antibiotics and improved public hygiene measures. Introduction. acute rheumatic fever (arf) is a nonsuppurative sequela that occurs two to four weeks following group a streptococcus (gas) pharyngitis and may consist of arthritis, carditis, chorea, erythema marginatum, and subcutaneous nodules. damage to cardiac valves may be chronic and progressive, resulting in cardiac decompensation.

Comments are closed.