Mnemonic 23 Jones Criteria For Acute Rheumatic Fever
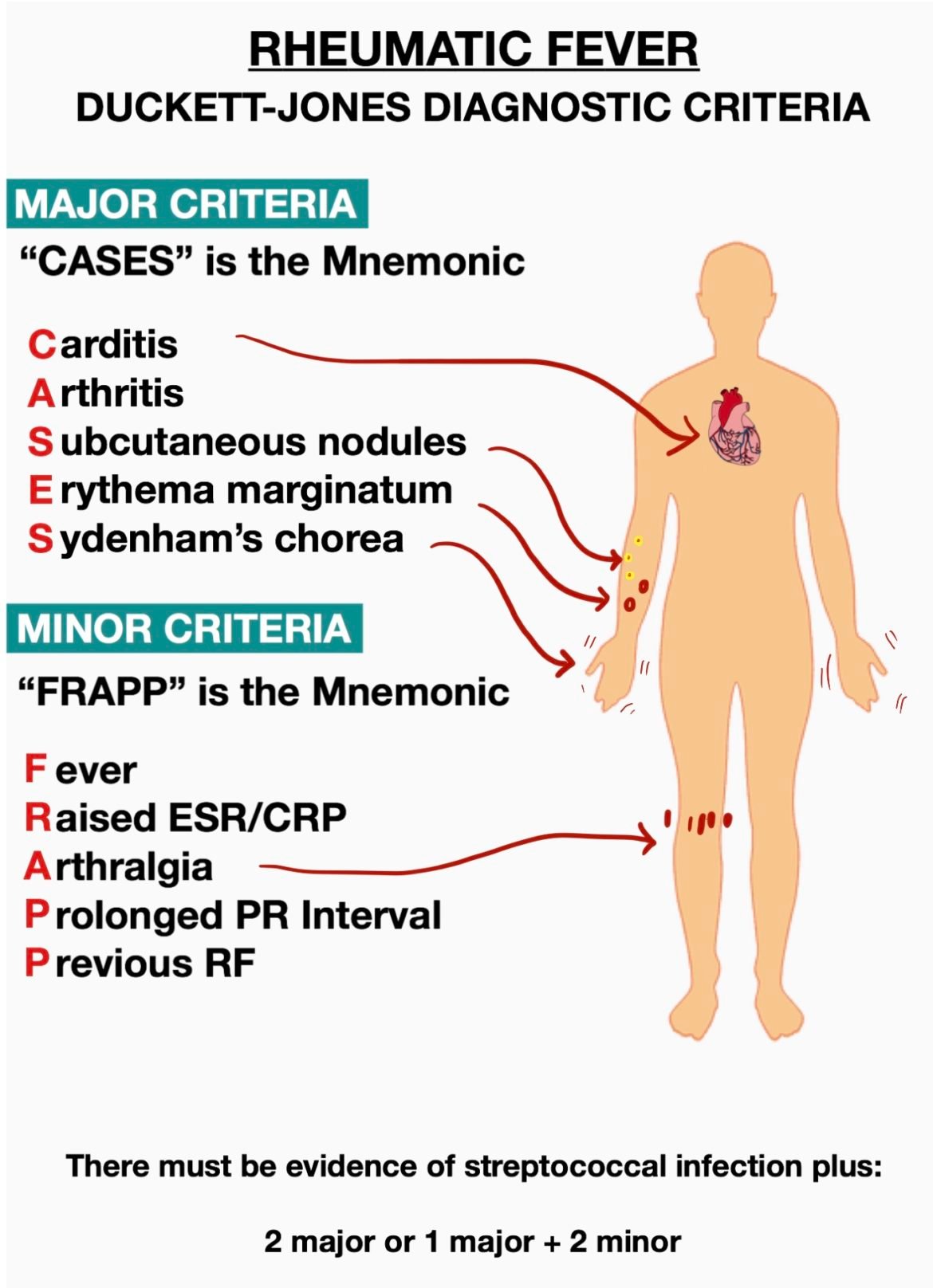
Rheumatic Fever Diagnostic Criteria Mnemonics Medical Junction Rheumatic fever occurs after a streptococcal infection (usually caused by group a beta hemolytic strep (gabhs)). it is an inflammatory condition that affects the joints, skin, heart and brain. major criteria are referred to as jones criteria and can be remembered by the mnemonic of the same name. The 2015 revised jones criteria consists of major and minor criteria (differing on whether the child belongs to a low risk or moderate and high risk population) and can be applied for diagnosis of initial or recurrent acute rheumatic fever, where evidence of group a streptococcus infection is present.

Rheumatic Fever Made Easy Including Jones Criteria And Mnemonic Share this post. “rheumatic fever (rf) is an inflammatory disease that can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain. the disease typically develops two to four weeks after a streptococcal throat infection.”. duckett jones diagnostic criteria: “the revised jones criteria are guidelines decided on by the american heart association to help. Rationale: although the incidence of acute rheumatic fever (arf) has declined in europe and north america over the past 4 6 decades, the disease remains one of the most important causes of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality among socially and economically disadvantaged populations all over the world, especially in developing countries that. Use clinical judgement regarding diagnosis and antibiotic prophylaxis in areas of high acute rheumatic fever incidence when lacking clinical evidence 2. acute rheumatic fever can be considered in cases of chorea and indolent, chronic carditis. this can be the case despite the lack of group a streptococcal laboratory confirmation or fullfillment. Background—acute rheumatic fever remains a serious healthcare concern for the majority of the world’s population despite its decline in incidence in europe and north america. the goal of this statement was to review the historic jones criteria used to diagnose acute rheumatic fever in the context of the current epidemiology of the disease and to update those criteria to also take into.

Mnemonic 23 Jones Criteria For Acute Rheumatic Fever Youtube Use clinical judgement regarding diagnosis and antibiotic prophylaxis in areas of high acute rheumatic fever incidence when lacking clinical evidence 2. acute rheumatic fever can be considered in cases of chorea and indolent, chronic carditis. this can be the case despite the lack of group a streptococcal laboratory confirmation or fullfillment. Background—acute rheumatic fever remains a serious healthcare concern for the majority of the world’s population despite its decline in incidence in europe and north america. the goal of this statement was to review the historic jones criteria used to diagnose acute rheumatic fever in the context of the current epidemiology of the disease and to update those criteria to also take into. In this video we cover rheumatic fever; what is it? rheumatic fever pathophysiology, the signs and symptoms of rheumatic fever as well as the diagnosis of rh. · minor criteria: pr interval, prolonged esr elevated arthralgias crp elevated elevated temperature (fever) · need 2 major or 1 major and 2 minor criteria, plus evidence of recent gas infection (throat cx, rapid antigen test, or rising strep antibody titer). people who viewed this page also visited:.

Revised Jones Criteria For Acute Rheumatic Fever Youtube In this video we cover rheumatic fever; what is it? rheumatic fever pathophysiology, the signs and symptoms of rheumatic fever as well as the diagnosis of rh. · minor criteria: pr interval, prolonged esr elevated arthralgias crp elevated elevated temperature (fever) · need 2 major or 1 major and 2 minor criteria, plus evidence of recent gas infection (throat cx, rapid antigen test, or rising strep antibody titer). people who viewed this page also visited:.

Comments are closed.