Memory And The Information Processing Model

Information Processing Theory Model Pdf Recall Memory Memory Information processing theory is a cornerstone of cognitive psychology that uses computers as a metaphor for how the human mind works. it was initially proposed in the mid 50s by american psychologists including george miller to explain how people process information into memory. The information processing model proposes three major stages of memory: sensory memory, short term memory, and long term memory. each stage plays a critical role in how information is processed and stored in our minds.

Information Processing Model Of Memory Traditionally, the most widely used model of information processing is the stage theory model, based on the work of atkinson and shiffrin (1968). the key elements of this model are that it views learning and memory as discontinuous and multi staged. According to the atkinson shiffrin model of memory, information passes through three distinct stages in order for it to be stored in long term memory. the three box is just one model of memory. Information processing is a cognitive learning theory that helps explain how individuals acquire, process, store, and retrieve information from memory. the cognitive architecture that facilitates the processing of information consists of three components: memory stores, cognitive processes, and metacognition. At the heart of learning lies the concept of how we absorb and retain information. the information processing model explains this through three main stages: sensory memory, working memory, and long term memory. let’s break each of these down to understand their role in learning.

Information Processing Model Sensory Memory Information Enters The Information processing is a cognitive learning theory that helps explain how individuals acquire, process, store, and retrieve information from memory. the cognitive architecture that facilitates the processing of information consists of three components: memory stores, cognitive processes, and metacognition. At the heart of learning lies the concept of how we absorb and retain information. the information processing model explains this through three main stages: sensory memory, working memory, and long term memory. let’s break each of these down to understand their role in learning. The information processing model shapes learning and memory by providing a framework that clarifies how attention, perception, and familiarity contribute to cognitive development. Information processing is a model for human thinking and learning, and it is a part of the resurgence of cognitive perspectives of learning. the cognitive perspective asserts that complex mental states affect human learning and behavior, that such mental states can be scientifically investigated. This paper establishes information processing theory as a crucial paradigm in understanding and treating learning disabilities, offering insights into the role of short term and episodic memory in processing information and its implications for cognitive psychologists.
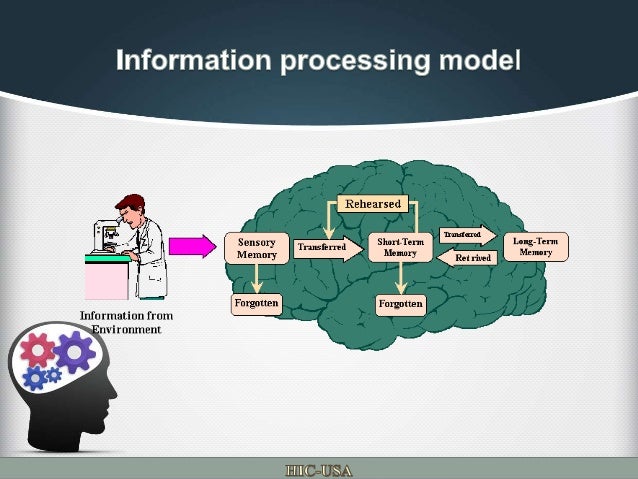
Information Processing Model Or Memory Model The information processing model shapes learning and memory by providing a framework that clarifies how attention, perception, and familiarity contribute to cognitive development. Information processing is a model for human thinking and learning, and it is a part of the resurgence of cognitive perspectives of learning. the cognitive perspective asserts that complex mental states affect human learning and behavior, that such mental states can be scientifically investigated. This paper establishes information processing theory as a crucial paradigm in understanding and treating learning disabilities, offering insights into the role of short term and episodic memory in processing information and its implications for cognitive psychologists.

Memory Information Processing Information Processing Model 1 Encoding This paper establishes information processing theory as a crucial paradigm in understanding and treating learning disabilities, offering insights into the role of short term and episodic memory in processing information and its implications for cognitive psychologists.

The Information Processing Model Of Memory Explained
Comments are closed.