Large Language Models Are Parallel Multilingual Learners Papers With Code
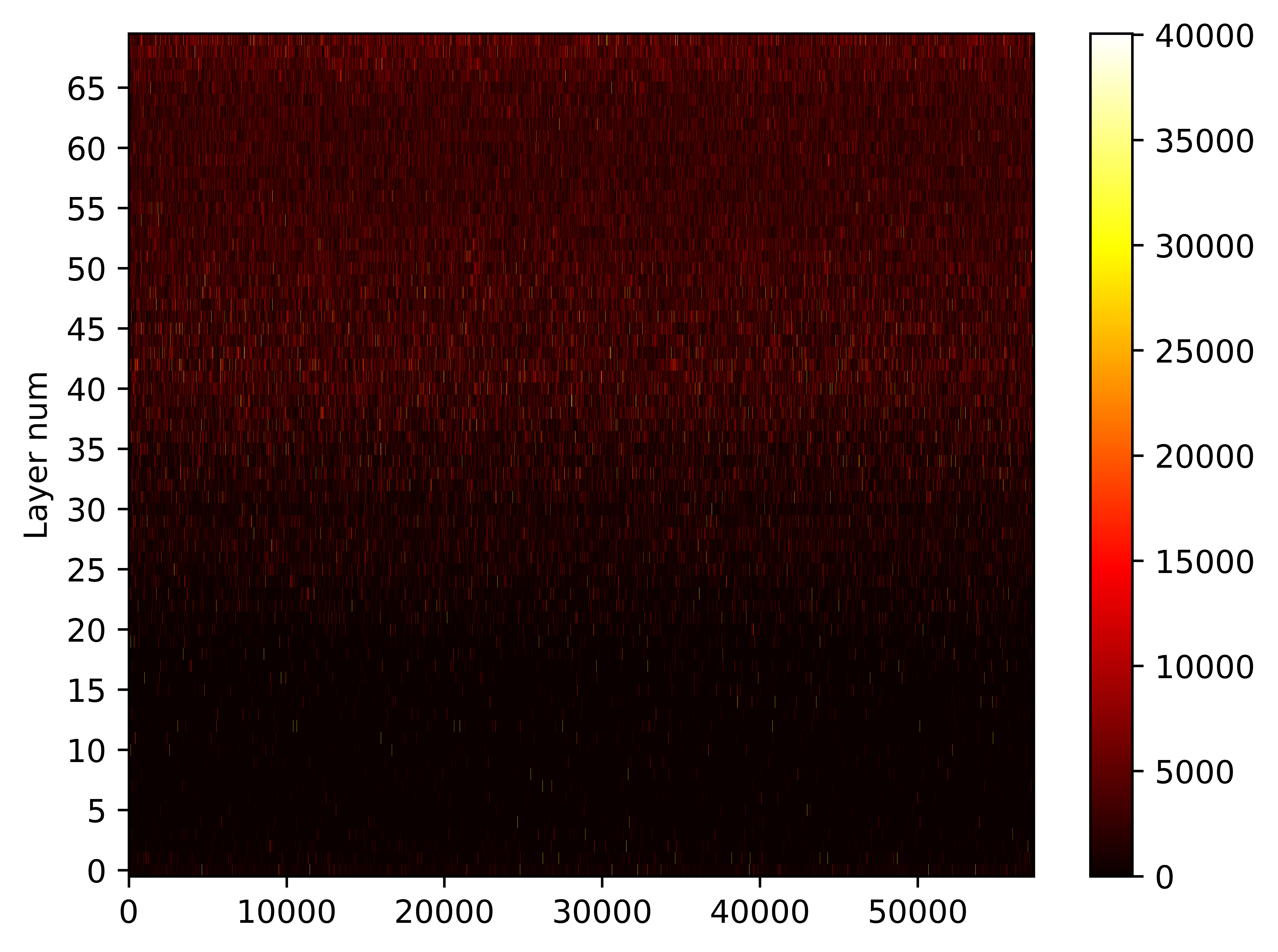
Large Language Models Are Parallel Multilingual Learners Papers With Code In this paper, we provide a comprehensive empirical analysis of various multilingual llms, benchmarking their performance across four tasks: sentiment analysis, machine translation, summarization and word level language identification. In this paper, we explore methods that make use of parallel multilingual input (pmi) in icl and explain how neurons are activated in this processing. there are two major findings. llms can benefit from receiving parallel in put in multiple languages.
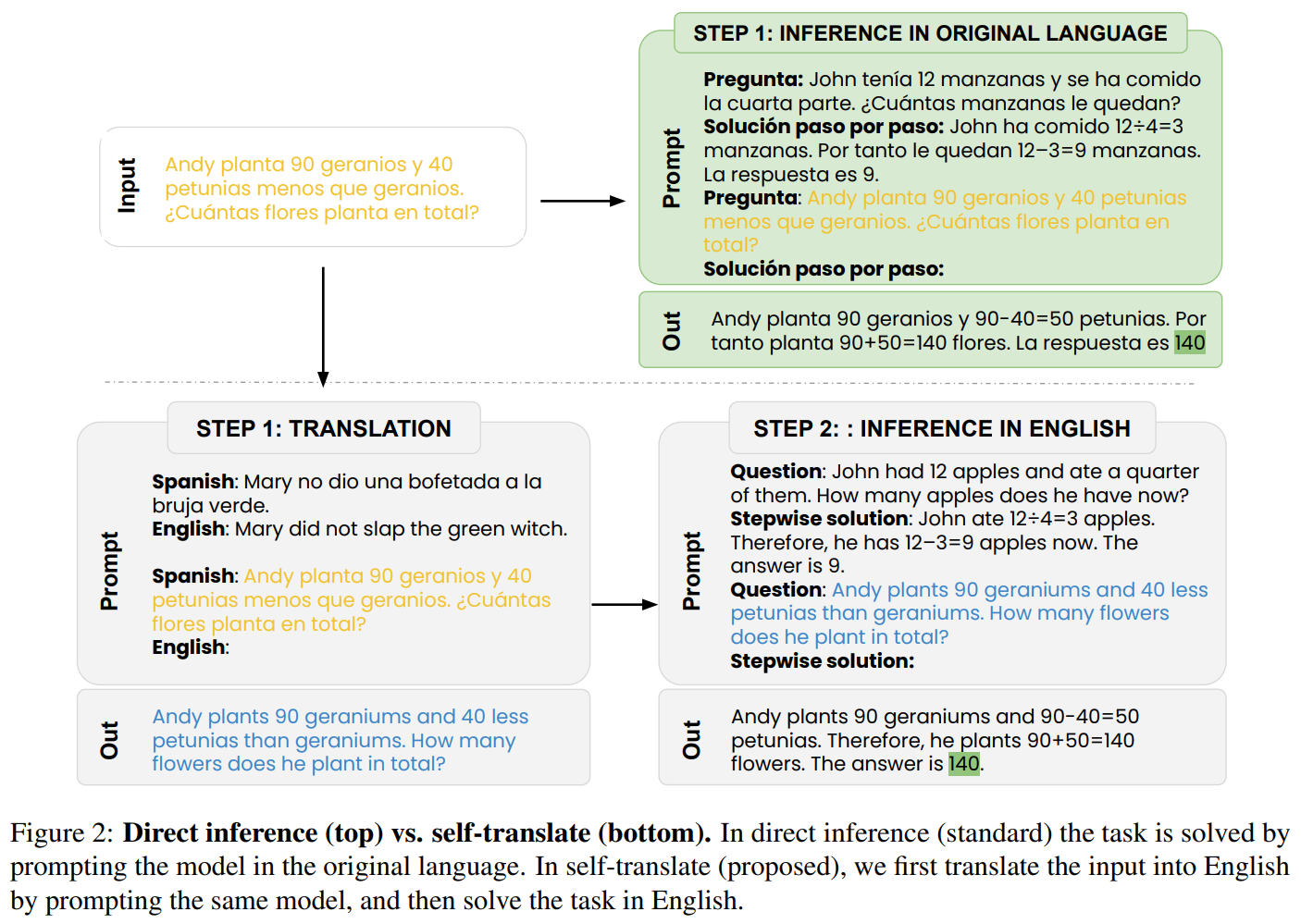
Do Multilingual Language Models Think Better In English Papers With Code In this study, we reveal an in context learning (icl) capability of multilingual large language models (llms): by translating the input to several languages, we provide parallel input in multiple languages (pim) to llms, which significantly enhances their comprehension abilities. In this study, we reveal an in context learn ing (icl) capability of multilingual large lan guage models (llms): by translating the in put to several languages, we provide parallel input in multiple languages (pim) to llms, which significantly enhances their comprehen sion abilities. The code of the paper revealing the parallel multilingual learning within large language models includes two parts. the first one is counting activated neurons in the multi layer perceptrons (mlps) of transformer models. To verify mwork, we introduce parallel language specific neuron detection (plnd) to identify activated neurons for inputs in different languages without any labeled data.

Language Models Are Few Shot Learners Papers With Code The code of the paper revealing the parallel multilingual learning within large language models includes two parts. the first one is counting activated neurons in the multi layer perceptrons (mlps) of transformer models. To verify mwork, we introduce parallel language specific neuron detection (plnd) to identify activated neurons for inputs in different languages without any labeled data. Recently, large language models (llms) have shown impressive language capabilities. while most of the existing llms have very unbalanced performance across different languages, multilingual alignment based on translation parallel data is an effective method to enhance the llms' multilingual capabilities. In this study, we reveal an in context learning (icl) capability of multilingual large language models (llms): by translating the input to several languages, we provide parallel input in multiple languages (pim) to llms, which significantly enhances their comprehension abilities. In this paper, we start by revealing that llms learn from parallel multilingual input (pmi). our comprehensive evaluation shows that pmi enhances the model's comprehension of the input, achieving superior performance than conventional in context learning (icl). Large language models (llms) have demonstrated impressive capabilities across diverse languages. this study explores how llms handle multilingualism.
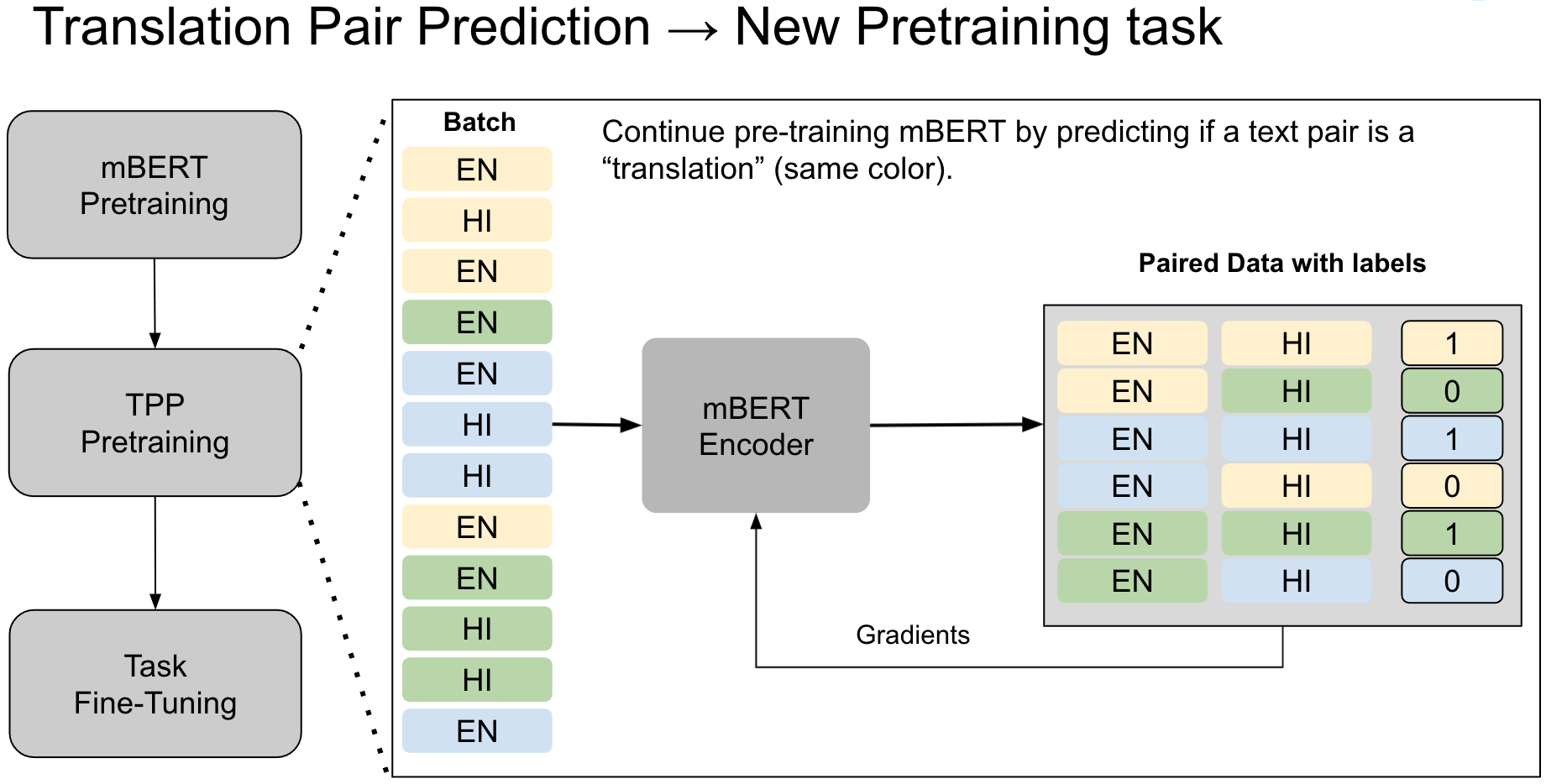
Improved Multilingual Language Model Pretraining For Social Media Text Recently, large language models (llms) have shown impressive language capabilities. while most of the existing llms have very unbalanced performance across different languages, multilingual alignment based on translation parallel data is an effective method to enhance the llms' multilingual capabilities. In this study, we reveal an in context learning (icl) capability of multilingual large language models (llms): by translating the input to several languages, we provide parallel input in multiple languages (pim) to llms, which significantly enhances their comprehension abilities. In this paper, we start by revealing that llms learn from parallel multilingual input (pmi). our comprehensive evaluation shows that pmi enhances the model's comprehension of the input, achieving superior performance than conventional in context learning (icl). Large language models (llms) have demonstrated impressive capabilities across diverse languages. this study explores how llms handle multilingualism.
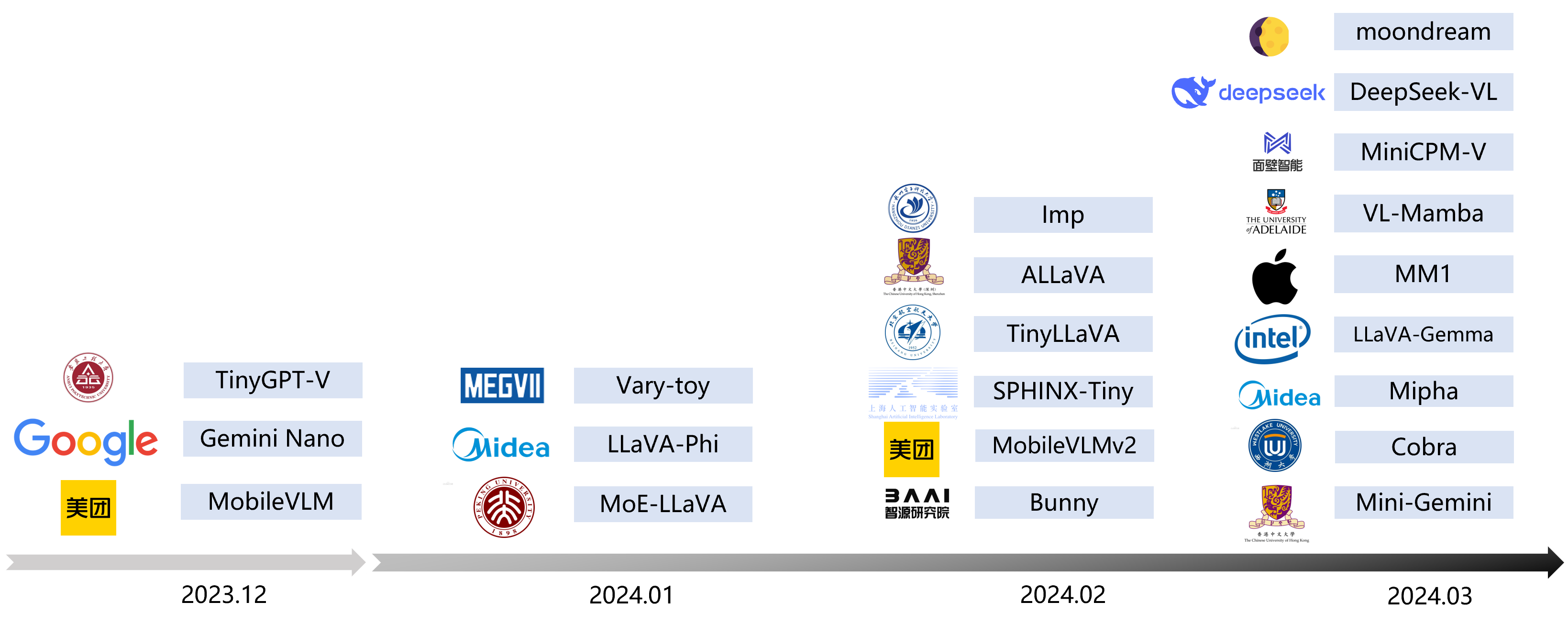
Efficient Multimodal Large Language Models A Survey Papers With Code In this paper, we start by revealing that llms learn from parallel multilingual input (pmi). our comprehensive evaluation shows that pmi enhances the model's comprehension of the input, achieving superior performance than conventional in context learning (icl). Large language models (llms) have demonstrated impressive capabilities across diverse languages. this study explores how llms handle multilingualism.
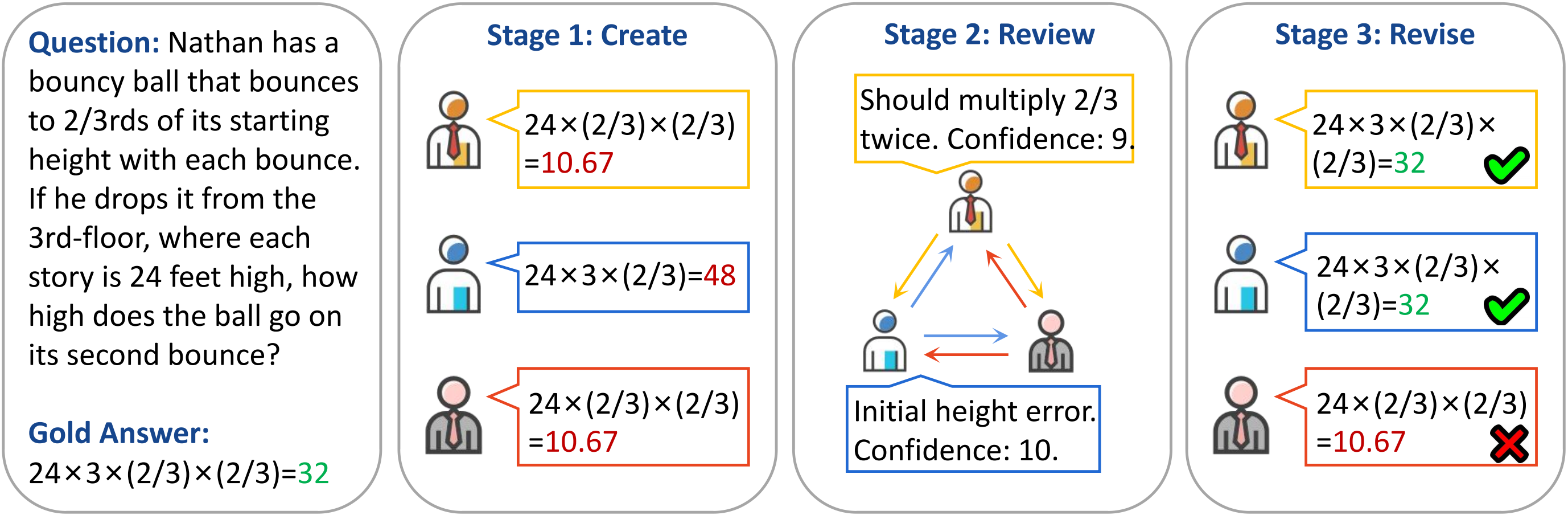
Towards Reasoning In Large Language Models Via Multi Agent Peer Review
Comments are closed.