Lambda Expressions In Java Full Simple Tutorial
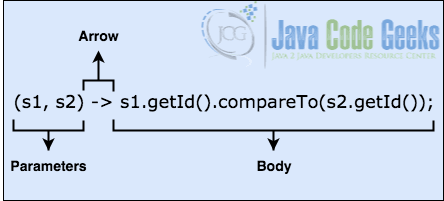
Lambda Expressions Java Tutorial Java Code Geeks A lambda function, or a small anonymous function, is a self contained block of functionality that can be passed around and used in your code. lambda has different names in different programming languages – lambda in python and kotlin, closure in swift, or block in c and objective c. What is a lambda expression in c 11? when would i use one? what class of problem do they solve that wasn't possible prior to their introduction? a few examples, and use cases would be useful.

Lambda Expressions Java Tutorial Java Code Geeks We're excited to announce the release of seven new lambda functions, as well as other improvements to this powerful functionality. Lambda is an anonymous function in python programming language, instead of bearing a def statement in the front it is simply called and written lambda. def mult2(x):. I saw some examples using built in functions like sorted, sum etc. that use key=lambda. what does lambda mean here? how does it work? for the general computer science concept of a lambda, see what. An easy way to perform an if in lambda is by using list comprehension. you can't raise an exception in lambda, but this is a way in python 3.x to do something close to your example:.
Java Lambda Expressions Advanced Java W3schools I saw some examples using built in functions like sorted, sum etc. that use key=lambda. what does lambda mean here? how does it work? for the general computer science concept of a lambda, see what. An easy way to perform an if in lambda is by using list comprehension. you can't raise an exception in lambda, but this is a way in python 3.x to do something close to your example:. Invalid comparison. first, you are not passing a lambda function to the filter version, which makes it default to the identity function. when defining if not none in the list comprehension you are defining a lambda function (notice the make function statement). I don't quite understand the syntax behind the sorted() argument: key=lambda variable: variable[0] isn't lambda arbitrary? why is variable stated twice in what looks like a dict?. Lambda overview there are three key pieces of =lambda to understand: lambda function components naming a lambda calling a lambda function lambda function components let’s look at an example which creates a basic lambda function. suppose we have the following formula: =lambda(x, x 122) in this, x is the argument you can pass in when calling the lambda, and x 122 is the logic. for example. As @unutbu mentioned, the issue is not with the number of lambda functions but rather with the keys in the dict passed to agg() not being in data as columns. op seems to have tried using named aggregation, which assign custom column headers to aggregated columns.

Java 8 Lambda Expressions Tutorial Lambda Expression Java Invalid comparison. first, you are not passing a lambda function to the filter version, which makes it default to the identity function. when defining if not none in the list comprehension you are defining a lambda function (notice the make function statement). I don't quite understand the syntax behind the sorted() argument: key=lambda variable: variable[0] isn't lambda arbitrary? why is variable stated twice in what looks like a dict?. Lambda overview there are three key pieces of =lambda to understand: lambda function components naming a lambda calling a lambda function lambda function components let’s look at an example which creates a basic lambda function. suppose we have the following formula: =lambda(x, x 122) in this, x is the argument you can pass in when calling the lambda, and x 122 is the logic. for example. As @unutbu mentioned, the issue is not with the number of lambda functions but rather with the keys in the dict passed to agg() not being in data as columns. op seems to have tried using named aggregation, which assign custom column headers to aggregated columns.
Comments are closed.