How To Graph Trigonometric Functions Trigonometry

Graphing Trigonometric Functions Pdf In graphing trigonometric functions, we typically use radian measure along the x x axis, so the graph would generally look like this: the graph of the standard sine function begins at the zero point, then rises to the maximum value of 1 between 0 and 73 7 3 radians. This trigonometry video tutorial explains how to graph sine and cosine functions using transformations, horizontal shifts phase shifts, vertical shifts, amplitude, and the period of the.

Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions Pdf Step 1: to draw the graph of a trigonometric function, convert it into its general form, y = a sin (bx c) d. step 2: now, identify the different parameters such as amplitude, phase shift, vertical shift, and period. Learn how to graph trigonometric functions, including their types sine, cosine, tangent, & their reciprocals, with their amplitude, period, examples, & diagrams. We can plot diagrams of different trigonometric functions with a range of their principal values. learn how to plot diagrams of trigonometric functions by the following step by step guide. This handout includes instructions for graphing processes of basic, amplitude shifts, horizontal shifts, and vertical shifts of trigonometric functions. you can navigate to specific sections of this handout by clicking the links below. the unit circle is a circle with a radius that equals 1.

Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions Pdf Trigonometric Functions We can plot diagrams of different trigonometric functions with a range of their principal values. learn how to plot diagrams of trigonometric functions by the following step by step guide. This handout includes instructions for graphing processes of basic, amplitude shifts, horizontal shifts, and vertical shifts of trigonometric functions. you can navigate to specific sections of this handout by clicking the links below. the unit circle is a circle with a radius that equals 1. Trig graphs are easy once you get the hang of them. once you learn the basic shapes, you shouldn't have much difficulty! the main problems a level students have, in my experience, are: remembering which is y = sin x and which is y = cos x. there's a trick to this i'll cover in a minute. This lesson shows how to graph the reciprocal trigonometric functions (y = csc x, y = sec x and y = cot x) using the y = sin x, y = cos x and y = tan x functions. how to use the unit circle to derive identities that are useful in graphing the reciprocal trigonometric functions?. Graphing trig functions requires finding the functions’ values at quadrantal angles and their periods. it is also important to find the trigonometric functions’ values at major angles, determine whether they are odd, even, or neither, and find the intervals over which they are positive and negative. At π 2 radians (90°), and at − π 2 (−90°), 3 π 2 (270°), etc, the function is officially undefined, because it could be positive infinity or negative infinity. the inverse sine, cosine and tangent graphs are: inverse sine. inverse cosine. inverse tangent. here is cosine and inverse cosine plotted on the same graph:.
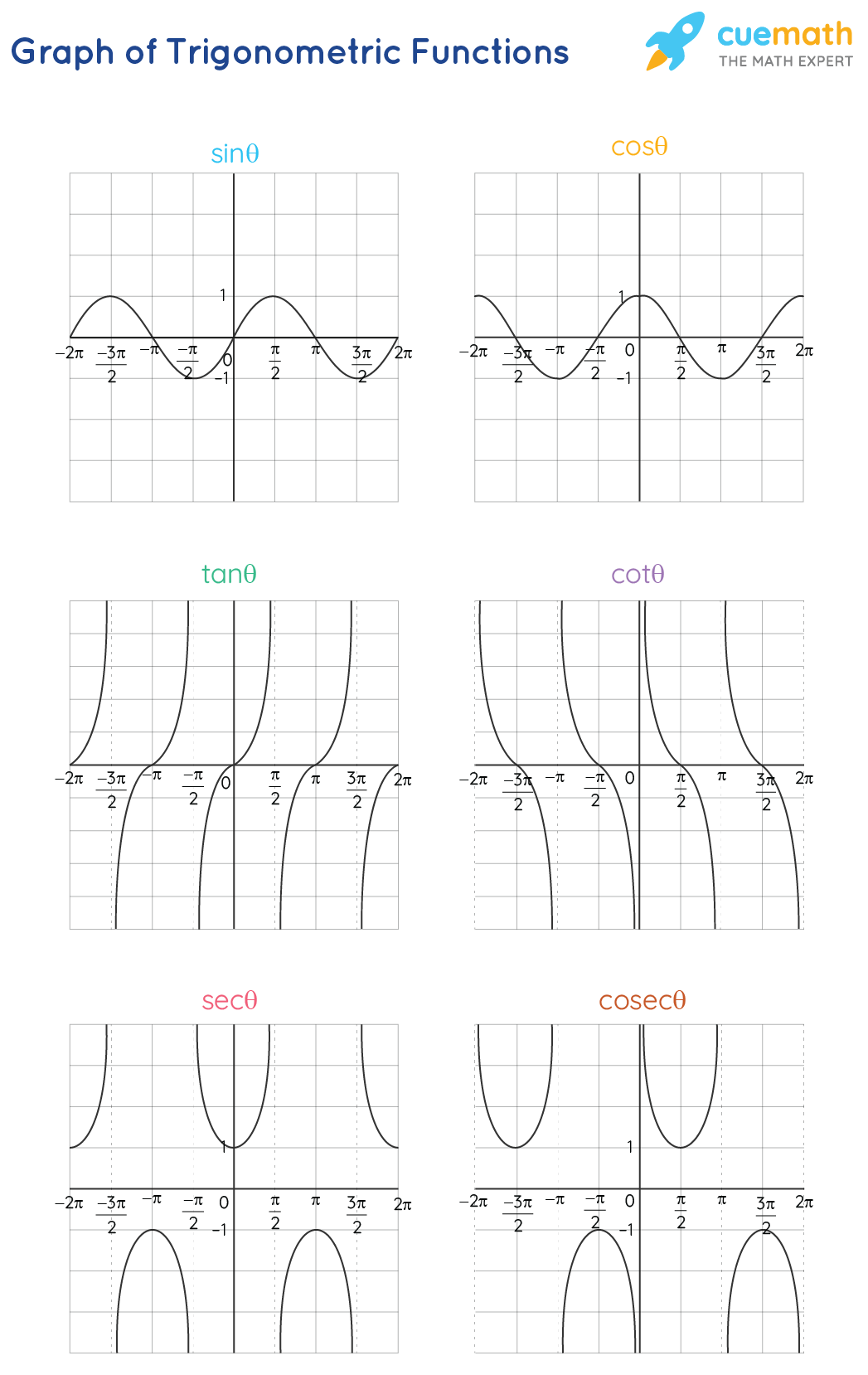
Trigonometric Functions Formulas Graphs Examples Values Trig graphs are easy once you get the hang of them. once you learn the basic shapes, you shouldn't have much difficulty! the main problems a level students have, in my experience, are: remembering which is y = sin x and which is y = cos x. there's a trick to this i'll cover in a minute. This lesson shows how to graph the reciprocal trigonometric functions (y = csc x, y = sec x and y = cot x) using the y = sin x, y = cos x and y = tan x functions. how to use the unit circle to derive identities that are useful in graphing the reciprocal trigonometric functions?. Graphing trig functions requires finding the functions’ values at quadrantal angles and their periods. it is also important to find the trigonometric functions’ values at major angles, determine whether they are odd, even, or neither, and find the intervals over which they are positive and negative. At π 2 radians (90°), and at − π 2 (−90°), 3 π 2 (270°), etc, the function is officially undefined, because it could be positive infinity or negative infinity. the inverse sine, cosine and tangent graphs are: inverse sine. inverse cosine. inverse tangent. here is cosine and inverse cosine plotted on the same graph:.
Comments are closed.