Git Init Git Add Git Commit Git Push Image To U

Git Init Git Add Git Commit Git Push Image To U I like to run git push set upstream origin master instead of git push origin master the first time. this allows me to just type git push or git pull instead of git push origin master every time. Shape your history into at least one commit by using git add to stage the existing files, and git commit to make the snapshot. once you have at least one commit, you can push to the remote and set up the tracking relationship for good with git push u origin main.

Mastering Git Git Add Git Commit Git Push Explained This guide focuses on the essential git commands `git add`, `git commit`, and `git push`, providing a clear understanding of each step and how they work together to manage your code changes. Learn how to set up a git repository with git init, connect to a remote, configure settings, and troubleshoot common issues—all in one beginner friendly guide. training more people? get your team access to the full datacamp for business platform. for business for a bespoke solution book a demo. The commands `git add`, `git commit`, and `git push` are used to stage changes, create a snapshot of those changes, and then upload the local repository to a remote server, respectively. here's the code snippet demonstrating these commands: git add . git commit m "your commit message" git push origin main understanding version control. ☁️ push code to github (first time) git push u origin main 📤 pushes the main branch to github and sets it as the default upstream branch. 🖼️ visuals for reference here are some screenshots that help illustrate the steps: 🔁 modifying or adding new files when you update existing files or add new ones, repeat the following: git add.

Git Complete Git Init Git Clone Git Add Commit Pull Push The commands `git add`, `git commit`, and `git push` are used to stage changes, create a snapshot of those changes, and then upload the local repository to a remote server, respectively. here's the code snippet demonstrating these commands: git add . git commit m "your commit message" git push origin main understanding version control. ☁️ push code to github (first time) git push u origin main 📤 pushes the main branch to github and sets it as the default upstream branch. 🖼️ visuals for reference here are some screenshots that help illustrate the steps: 🔁 modifying or adding new files when you update existing files or add new ones, repeat the following: git add. Third, we will use a few ‘git commands’ to initialize a local repository and push them to a remote repository that can be accessed through the github website. below we run each of these. In this blog, we’ll walk you through the process of committing and pushing code in git, along with best practices and troubleshooting tips to ensure a smooth workflow. a commit in git represents a snapshot of your project at a specific point in time. commits are made locally, meaning changes are saved only on your machine. You can use git to track the different versions of a file by first adding it so that git is aware of the file you are interested in, second committing the changes you made. Most of the time, you will see git add . followed by git commit m "commit message". there is a shorthand for this using git commit am "commit message". sometimes, your pull request pipeline may fail due to some initialization issues.
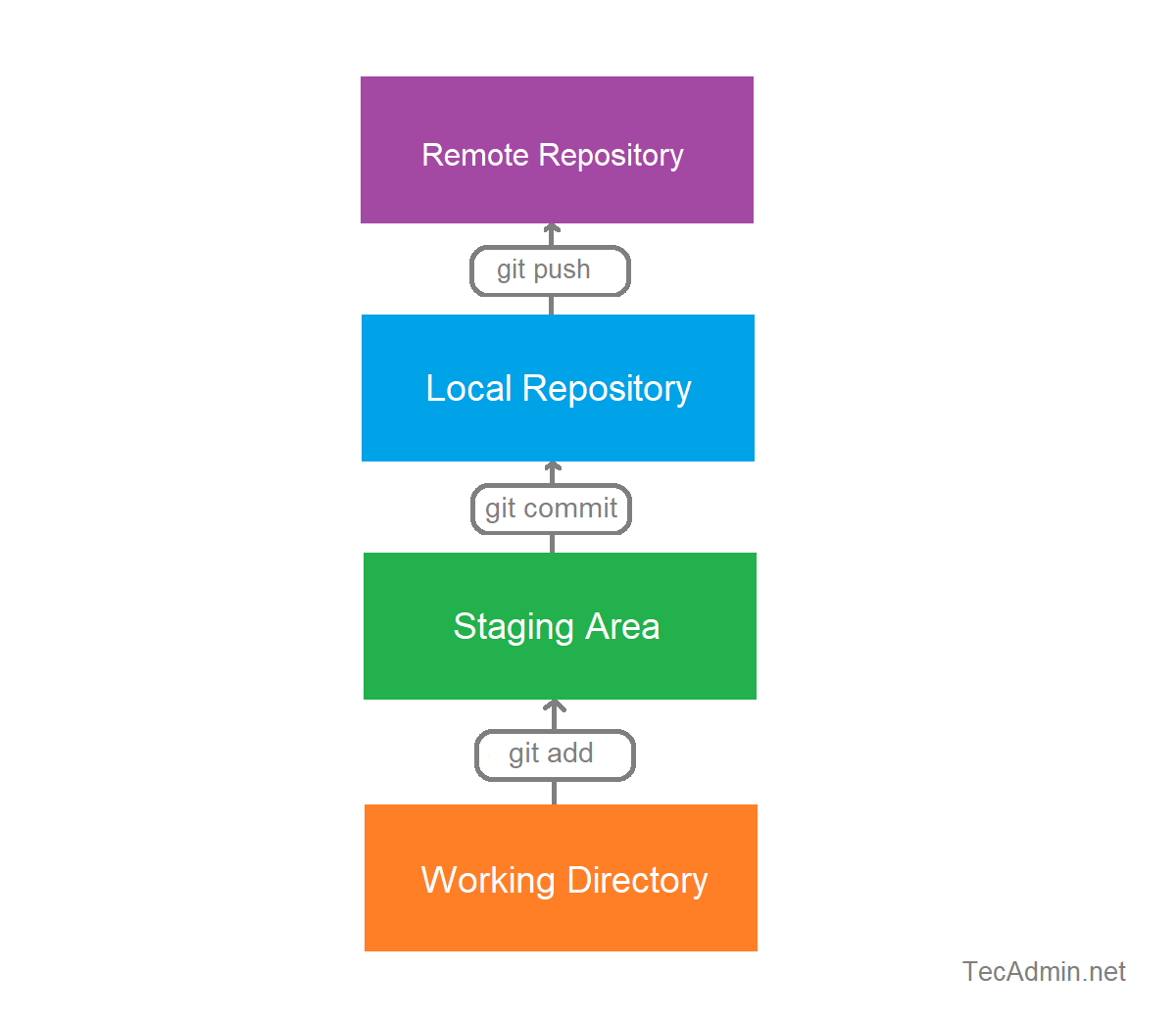
Git Add Git Commit Git Push Image To U Third, we will use a few ‘git commands’ to initialize a local repository and push them to a remote repository that can be accessed through the github website. below we run each of these. In this blog, we’ll walk you through the process of committing and pushing code in git, along with best practices and troubleshooting tips to ensure a smooth workflow. a commit in git represents a snapshot of your project at a specific point in time. commits are made locally, meaning changes are saved only on your machine. You can use git to track the different versions of a file by first adding it so that git is aware of the file you are interested in, second committing the changes you made. Most of the time, you will see git add . followed by git commit m "commit message". there is a shorthand for this using git commit am "commit message". sometimes, your pull request pipeline may fail due to some initialization issues.

Git Add Git Commit Git Push Image To U You can use git to track the different versions of a file by first adding it so that git is aware of the file you are interested in, second committing the changes you made. Most of the time, you will see git add . followed by git commit m "commit message". there is a shorthand for this using git commit am "commit message". sometimes, your pull request pipeline may fail due to some initialization issues.
Comments are closed.