Float And Double Data Type In Java Java Data Types Java Tutorial For Beginners H2k Infosys
Java Float Doublevalue Method Example With type float, on the other hand, alarming looking issues with roundoff crop up all the time. and the thing that's not necessarily different between type float and double is execution speed. Note that float can approximately represent the latter and still smaller values it's just about 7 decimals of precision after the first nonzero digit! if you're going to use a fixed epsilon, you should really choose it according to the requirements of the particular piece of code where you use it.
Float Double Time Float Data Type Java What is the inclusive range of float and double in java? why are you not recommended to use float or double for anything where precision is critical?. For a given ieee 754 floating point number x, if 2^e <= abs(x) < 2^(e 1) then the distance from x to the next largest representable floating point number (epsilon) is: epsilon = 2^(e 52) % for a 64 bit float (double precision) epsilon = 2^(e 23) % for a 32 bit float (single precision) epsilon = 2^(e 10) % for a 16 bit float (half precision) the above equations allow us to compute the following. Numpy's dtype documentation only shows "x bits exponent, y bits mantissa" for each float type, but i couldn't translate that to exactly how many digits before after the decimal point. is. You cannot properly round the number itself, because float (and double) aren't decimal floating point they are binary floating point so rounding to decimal positions is meaningless. you can round the output, however.
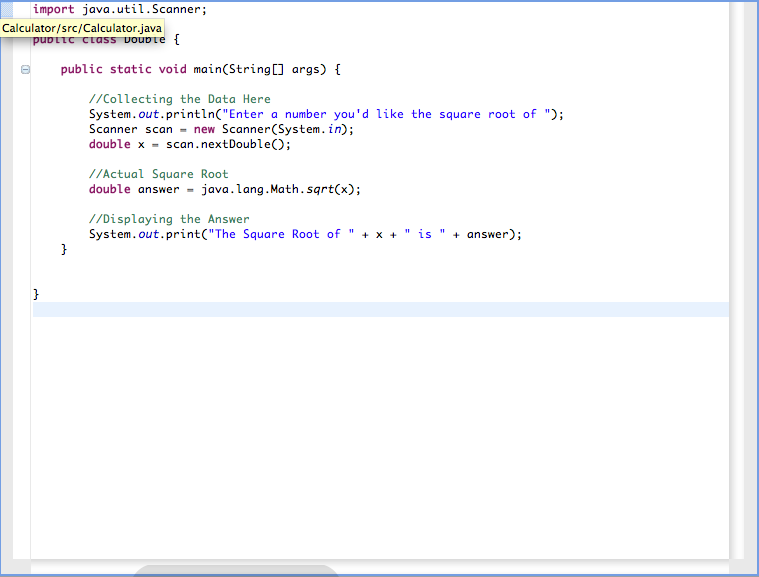
Java Tutorial Ii Data Types Part Iv Double Byte Revel Numpy's dtype documentation only shows "x bits exponent, y bits mantissa" for each float type, but i couldn't translate that to exactly how many digits before after the decimal point. is. You cannot properly round the number itself, because float (and double) aren't decimal floating point they are binary floating point so rounding to decimal positions is meaningless. you can round the output, however. Float stores floating point values, that is, values that have potential decimal places int only stores integral values, that is, whole numbers so while both are 32 bits wide, their use (and representation) is quite different. you cannot store 3.141 in an integer, but you can in a float. dissecting them both a little further: in an integer, all bits except the leftmost one are used to store the. What is the difference between decimal, float and double in ? when would someone use one of these?. There is an operator missing, likely a *: 3.7 need something here (prof[x]) the "is not callable " occurs because the parenthesis and lack of operator which would have switched the parenthesis into precedence operators make python try to call the result of 3.7 (a float) as a function, which is not allowed. the parenthesis are also not needed in this case, the following may be. 1 the main difference between float and double is precision. has more info about single precision (float) and double precision.
Comments are closed.