Dynamic Random Access Memory Dram Part 3 Binary Decoders

Dram Dynamic Random Access Memory Type Random Access Semiconductor This video covers the role of the row address decoder and the workings of generic binary decoders. it also explains how a binary decoder can be built using combinational logic. To access dynamic memory, one must select a row address and then assert a pin called ras (row address select). this will both latch a row address and cause that particular row of memory locations to be read to a temporary buffer.
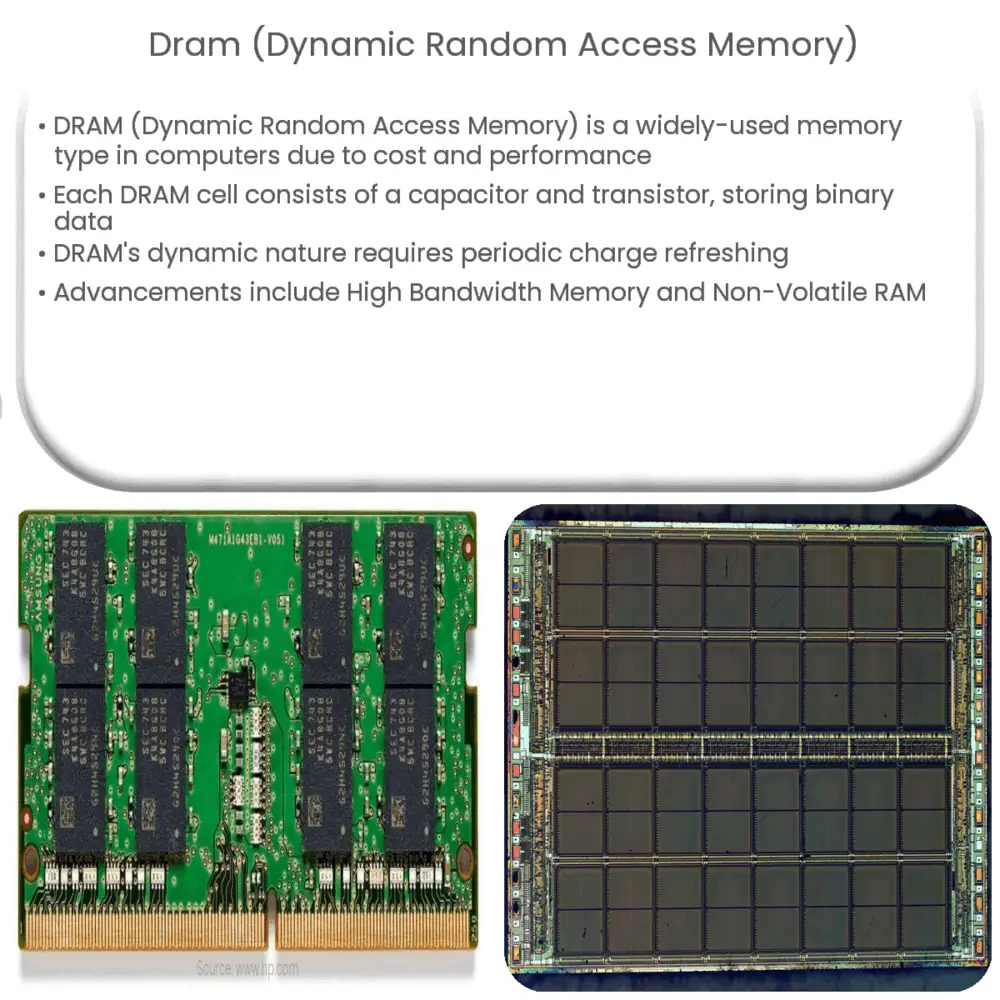
Dram Dynamic Random Access Memory How It Works Application Dynamic random access memory (dram) is a type of random access memory that stores each bit of data in a separate capacitor within an integrated circuit. since real capacitors leak charge, the information eventually fades unless the capacitor charge is refreshed periodically. Dram is a major power sink. complex interface. high power. dram used to be the main driver for process scaling, now it’s flash. power is now a major concern. historical foot note: intel got its start as a dram company, but got out of it when it became a commodity. How does a processor or memory controller tell the dram to return or store specific data in a specific location? understanding the commands sent to a dram chip is the first step in actually designing a system that uses dram. But larger amounts of memory are built using either srams access memories) or drams (dynamic random access memories). we srams, which are somewhat simpler, and then turn to drams. dram). srams are faster than drams, but less dense and more expensive per bit.

Dram Pdf Dynamic Random Access Memory Flash Memory How does a processor or memory controller tell the dram to return or store specific data in a specific location? understanding the commands sent to a dram chip is the first step in actually designing a system that uses dram. But larger amounts of memory are built using either srams access memories) or drams (dynamic random access memories). we srams, which are somewhat simpler, and then turn to drams. dram). srams are faster than drams, but less dense and more expensive per bit. Accessing any bit in dram given its row and column address is analogous to locating the bit in the memory array given its (x,y) coordinates. the actual physical structure of dram differs from this (see next slides), but it is based on this fundamental logical structure. The document discusses dynamic random access memory (dram). dram uses a capacitor and transistor to store each bit of data, which allows it to be implemented using less space than sram. Dynamic random access memory dram part 3 binary decoders lesson with certificate for computer science courses. Random access memory array organization. each memory cell • stores one bit of binary information (”0“ or ”1“ logic) • shares common connections with other cells: rows, columns memory array • memory storage cells • address decoders. 5. institute of microelectronic. 17: semiconductor memories systems.

Dram Dynamic Random Access Memory Process Flow Summary Of Key Ideas Accessing any bit in dram given its row and column address is analogous to locating the bit in the memory array given its (x,y) coordinates. the actual physical structure of dram differs from this (see next slides), but it is based on this fundamental logical structure. The document discusses dynamic random access memory (dram). dram uses a capacitor and transistor to store each bit of data, which allows it to be implemented using less space than sram. Dynamic random access memory dram part 3 binary decoders lesson with certificate for computer science courses. Random access memory array organization. each memory cell • stores one bit of binary information (”0“ or ”1“ logic) • shares common connections with other cells: rows, columns memory array • memory storage cells • address decoders. 5. institute of microelectronic. 17: semiconductor memories systems.

Embedded Dram Pdf Dynamic Random Access Memory System On A Chip Dynamic random access memory dram part 3 binary decoders lesson with certificate for computer science courses. Random access memory array organization. each memory cell • stores one bit of binary information (”0“ or ”1“ logic) • shares common connections with other cells: rows, columns memory array • memory storage cells • address decoders. 5. institute of microelectronic. 17: semiconductor memories systems.
Comments are closed.