Dilution Problems Chemistry Molarity Concentration Examples Formula Equations
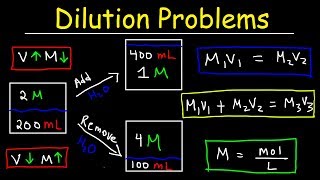
Dilution Problems Chemistry Molarity U0026 Concentratio Doovi Problem #5: a 40.0 ml volume of 1.80 m fe (no 3) 3 is mixed with 21.5 ml of 0.808m fe (no 3) 3 solution. calculate the molar concentration of the final solution. This chemistry video tutorial explains how to solve common dilution problems using a simple formula using concentration or molarity with volume. this video also provides the equations.

Solved Dilution Problems Useful Equations And Facts 1 Csv Chegg Dilution is a related concept often used to adjust solution concentrations. dilution involves adding more solvent to reduce the solution’s concentration. the number of moles of the solute remains constant, but the total volume increases, decreasing the solution’s concentration. What is the molarity of the diluted solution when each of the following solutions is diluted to the given final volume? 1.00 l of a 0.250 m solution of fe (no 3) 3 is diluted to a final volume of 2.00 l. Sample problem: dilution of a stock solution nitric acid (hno 3) is a powerful and corrosive acid. when ordered from a chemical supply company, its molarity is 16 m. how much of the stock solution of nitric acid needs to be used to make 8.00 l of a 0.50 m solution? step 1: list the known quantities and plan the problem. known stock hno 3 = 16 m. Chemical quantities & aqueous reactions dilutions. struggling with general chemistry? join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams! watch the first video.

Dilution Problems Chemistry Tutorial Chemistry Notes Chemistry Sample problem: dilution of a stock solution nitric acid (hno 3) is a powerful and corrosive acid. when ordered from a chemical supply company, its molarity is 16 m. how much of the stock solution of nitric acid needs to be used to make 8.00 l of a 0.50 m solution? step 1: list the known quantities and plan the problem. known stock hno 3 = 16 m. Chemical quantities & aqueous reactions dilutions. struggling with general chemistry? join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams! watch the first video. Dilutions worksheet 1) if i have 340 ml of a 0.5 m nabr solution, what will the concentration be if i add 560 ml more water to it? 2) if i dilute 250 ml of 0.10 m lithium acetate solution to a volume of 750 ml, what will the concentration of this solution be?. A dilution is a process where the concentration of a solution is lowered by adding solvent to the solution without adding more solute. these dilution example problems show how to perform the calculations needed to make a diluted solution. Dilution: c1v1 = c2v2 note: concentrations and volumes can be in any units, as long as both concentrations are in the same units as each other, and both volumes are in the same units as each other. Example: if a 20 mg ml sugar solution were diluted 1:4 and then the new sugar solution were diluted 1:5, the concentration of the third solution would be 1 mg ml. try working this as a sequence of two separate dilution problems, and then you'll see why the shortcut works: 20 mg ml x 1 4 x 1 5 = 1 mg ml. the total dilution here is 1 to 20.

Molarity And Dilution Equations Dilutions worksheet 1) if i have 340 ml of a 0.5 m nabr solution, what will the concentration be if i add 560 ml more water to it? 2) if i dilute 250 ml of 0.10 m lithium acetate solution to a volume of 750 ml, what will the concentration of this solution be?. A dilution is a process where the concentration of a solution is lowered by adding solvent to the solution without adding more solute. these dilution example problems show how to perform the calculations needed to make a diluted solution. Dilution: c1v1 = c2v2 note: concentrations and volumes can be in any units, as long as both concentrations are in the same units as each other, and both volumes are in the same units as each other. Example: if a 20 mg ml sugar solution were diluted 1:4 and then the new sugar solution were diluted 1:5, the concentration of the third solution would be 1 mg ml. try working this as a sequence of two separate dilution problems, and then you'll see why the shortcut works: 20 mg ml x 1 4 x 1 5 = 1 mg ml. the total dilution here is 1 to 20.
Comments are closed.