Digitization Sampling Quantization Mechatronics
Digitization Sampling Quantization Mechatronics Digitization is the process of representing various types of information in a form that can be stored and processed by a digital device. it is the combined operations of sampling and quantization, also called analog to digital (a d) conversion. The process of digitizing the domain is called sampling and the process of digitizing the range is called quantization. most devices we encounter deal with both analog and digital signals.
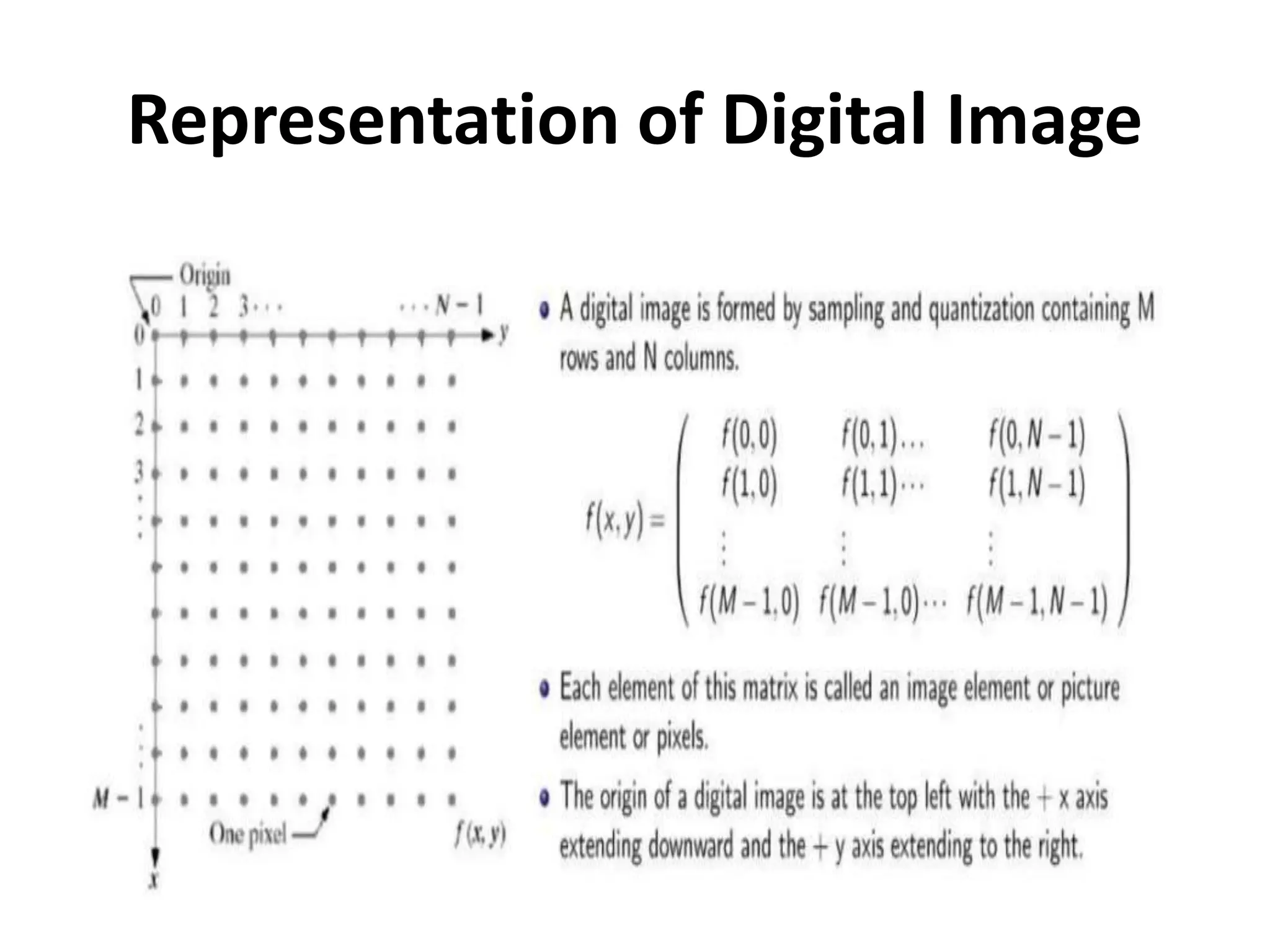
Sampling And Quantization In Digitization Ppt Quantization: discrete representations for amplitudes we measure discrete amplitudes in bits. we hear sounds that range in amplitude from 1,000,000 to 1. how many bits are needed to represent this range? we hear sounds that range in amplitude from 1,000,000 to 1. There are many different ways in which an analog signal may be turned into a digital form. several different techniques have evolved for dealing with different system requirements. these include flash, staircase, successive approximation, and delta sigma forms. When we want to represent such a sinosoid in the digital domain, we have to do two things: sampling and quantization which are described in turn. the first thing we have to do, is to obtain signal values from the continuous signal at regular time intervals. this process is known as sampling. Digitization is the process of converting continuous time signals into a sequence of numbers. this is a two stage process involving sampling in time and quantizing for representation of the samples by a finite number of digits or bits.

Sampling And Quantization In Digitization Ppt When we want to represent such a sinosoid in the digital domain, we have to do two things: sampling and quantization which are described in turn. the first thing we have to do, is to obtain signal values from the continuous signal at regular time intervals. this process is known as sampling. Digitization is the process of converting continuous time signals into a sequence of numbers. this is a two stage process involving sampling in time and quantizing for representation of the samples by a finite number of digits or bits. We will discuss the process of converting analog signals to digital codes (integers and floating point numbers), as well as the reverse process of reconstructing analog signals from those digital codes. Motivation• why does every engineer need to know about digitization –sampling, aliasing, bits and bytes, and quantization?•. first, as an educated person, one should know how all thedigital devices we use every day – computers, cell phones,tvs and cameras, cd and dvd players – work!•. Understanding the differences and interplay between image sampling and quantization is crucial for anyone working with digital images. while sampling determines how finely the image is divided spatially, quantization determines how precisely the intensity values are represented. Quantization and sampling are two fundamental processes in digital signal processing. sampling refers to the process of converting a continuous time signal into a discrete time signal by taking samples at regular intervals. this allows us to represent the signal in a digital format.
Comments are closed.