Diffusion Models Explained In 4 Difficulty Levels

Diffusion Models A Simple Guide To Get Started Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. diffusion is driven by a gradient in gibbs free energy or chemical potential. Diffusion, process resulting from random motion of molecules by which there is a net flow of matter from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration. a familiar example is the perfume of a flower that quickly permeates the still air of a room.

Diffusion Models Explained In 4 Difficulty Levels R Learnmachinelearning Diffusion is a physical process that refers to the net movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to one of lower concentration. the material that diffuses could be a solid, liquid or gas. Diffusion is a fundamental process involving the movement of particles, such as atoms, ions, or molecules, from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration. this movement continues until the concentration is uniform throughout the medium, reaching equilibrium. “diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration down the concentration gradient.” read on to explore what is diffusion and the different types of diffusion. Diffusion is the process by which particles of one substance spread out through the particles of another substance. diffusion is how smells spread out through the air and how concentrated.

Diffusion Models Broken Down By 5 Units By Suchismit Medium “diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration down the concentration gradient.” read on to explore what is diffusion and the different types of diffusion. Diffusion is the process by which particles of one substance spread out through the particles of another substance. diffusion is how smells spread out through the air and how concentrated. Diffusion is the movement of a molecule down a concentration gradient, from an area of its high concentration to an area of its low concentration. this process is passive, i.e. it requires no input of additional energy; the concentration gradient alone is enough to drive the process. Diffusion stands out as a core principle in biology, crucial for grasping how molecules move within and between cells. this process naturally enables particles to migrate from areas of high concentration to those of low concentration, leading to an even distribution. Diffusion, in biochemistry, refers to one of many processes by which molecules can move into and out of cells through the plasma membrane, or cross membranes within the cell, such as the nuclear membrane or the membrane that encloses mitochondria. think of diffusion as a "drifting" movement. Diffusion is the tendency of molecules to spread into an available area. learn about the different types of diffusion, passive, facilitated and osmosis.
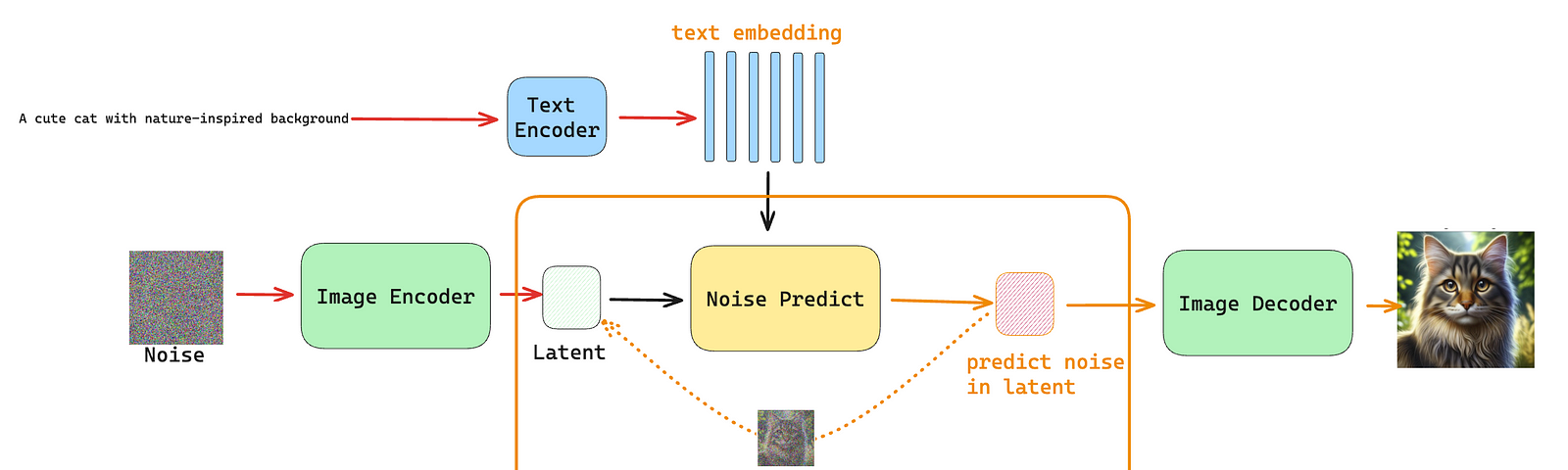
Diffusion Models The Deep Hub Medium Diffusion is the movement of a molecule down a concentration gradient, from an area of its high concentration to an area of its low concentration. this process is passive, i.e. it requires no input of additional energy; the concentration gradient alone is enough to drive the process. Diffusion stands out as a core principle in biology, crucial for grasping how molecules move within and between cells. this process naturally enables particles to migrate from areas of high concentration to those of low concentration, leading to an even distribution. Diffusion, in biochemistry, refers to one of many processes by which molecules can move into and out of cells through the plasma membrane, or cross membranes within the cell, such as the nuclear membrane or the membrane that encloses mitochondria. think of diffusion as a "drifting" movement. Diffusion is the tendency of molecules to spread into an available area. learn about the different types of diffusion, passive, facilitated and osmosis.

What Are Diffusion Models Baeldung On Computer Science Diffusion, in biochemistry, refers to one of many processes by which molecules can move into and out of cells through the plasma membrane, or cross membranes within the cell, such as the nuclear membrane or the membrane that encloses mitochondria. think of diffusion as a "drifting" movement. Diffusion is the tendency of molecules to spread into an available area. learn about the different types of diffusion, passive, facilitated and osmosis.
Comments are closed.