Difference Between Alpha Helix And Beta Pleated Sheet
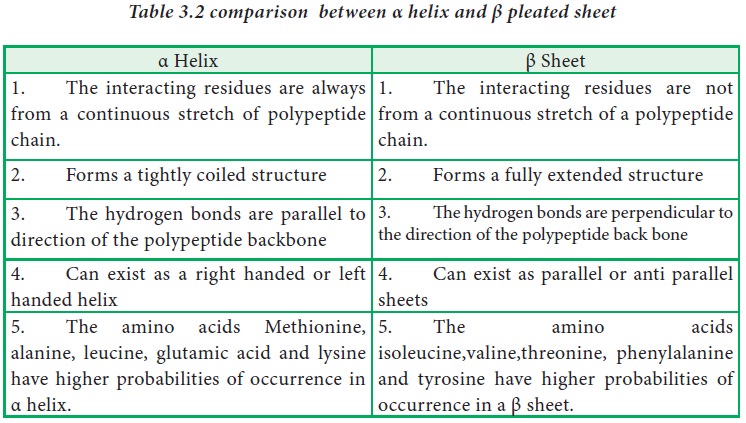
Difference Between Alpha Helix And Beta Pleated Sheet 58 Off Alpha helix: alpha helix prefers the amino acid side chains, which can cover and protect the backbone h bonds in the core of the helix. beta pleated sheet: the extended structure leaves the maximum space free for the amino acid side chains. Alpha helix and beta pleated sheets are types of the secondary structure of the protein. they both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. this section will discuss the protein, types of protein, and the primary and secondary protein structures, i.e. alpha helix and beta pleated sheets.
Difference Between Alpha Helix And Beta Pleated Sheet 58 Off Watch our summarized 5 minute video on alpha helix and beta pleated sheet. it is held together by hydrogen bonds between the c=o (carbonyl oxygen) of residue 1 and the nh (amide h) of residue 4. it is held by hydrogen bond between the n−h groups in the backbone of one strand and c=o groups in the backbone of the adjacent strands. Alpha helix and beta pleated sheet are secondary structures of proteins, differing in shape: an alpha helix is a spiral, while a beta pleated sheet is folded or pleated. the alpha helix is a right handed coiled strand, typically linked by hydrogen bonds. The alpha helix is a right handed coil, while the beta pleated sheet is a sheet like arrangement. the alpha helix is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between amino acid residues four positions down the chain, while the beta pleated sheet forms hydrogen bonds between adjacent strands. In this definition of alpha helix, sheets are characterised through their tight pleats, while in beta pleated sheets, they have looser pleats. additionally, alpha helix sheets are much less likely to stretch than beta pleated sheets.

Difference Between Alpha Helix And Beta Pleated Sheet Alpha Helix And The alpha helix is a right handed coil, while the beta pleated sheet is a sheet like arrangement. the alpha helix is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between amino acid residues four positions down the chain, while the beta pleated sheet forms hydrogen bonds between adjacent strands. In this definition of alpha helix, sheets are characterised through their tight pleats, while in beta pleated sheets, they have looser pleats. additionally, alpha helix sheets are much less likely to stretch than beta pleated sheets. Understanding the differences between the alpha helix and the beta pleated sheet is pivotal for comprehending protein folding, stability, and function. these secondary structures represent distinct ways in which a polypeptide chain can arrange itself to maximize hydrogen bonding potential within the protein backbone. while both structures rely on hydrogen bonds for stability, they differ. There are two types of secondary structure (i) alpha helix (ii) beta pleated sheet. both structures are formed by hydrogen bonding between carbonyle group of one amino acid and amine. Alpha helix and beta pleated sheets are the common types of secondary protein structures. both structures are joined together by hydrogen bonds but differ in appearance and arrangement. Alpha helices are formed when the polypeptide chain twists into a spiral shape due to hydrogen bonds between the backbone amide and carbonyl groups. beta sheets, on the other hand, are created when adjacent segments of the polypeptide chain fold into a pleated, sheet like conformation, also stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
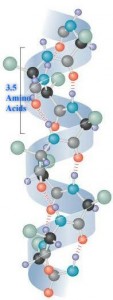
Difference Between Alpha Helix And Beta Pleated Sheet Understanding the differences between the alpha helix and the beta pleated sheet is pivotal for comprehending protein folding, stability, and function. these secondary structures represent distinct ways in which a polypeptide chain can arrange itself to maximize hydrogen bonding potential within the protein backbone. while both structures rely on hydrogen bonds for stability, they differ. There are two types of secondary structure (i) alpha helix (ii) beta pleated sheet. both structures are formed by hydrogen bonding between carbonyle group of one amino acid and amine. Alpha helix and beta pleated sheets are the common types of secondary protein structures. both structures are joined together by hydrogen bonds but differ in appearance and arrangement. Alpha helices are formed when the polypeptide chain twists into a spiral shape due to hydrogen bonds between the backbone amide and carbonyl groups. beta sheets, on the other hand, are created when adjacent segments of the polypeptide chain fold into a pleated, sheet like conformation, also stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
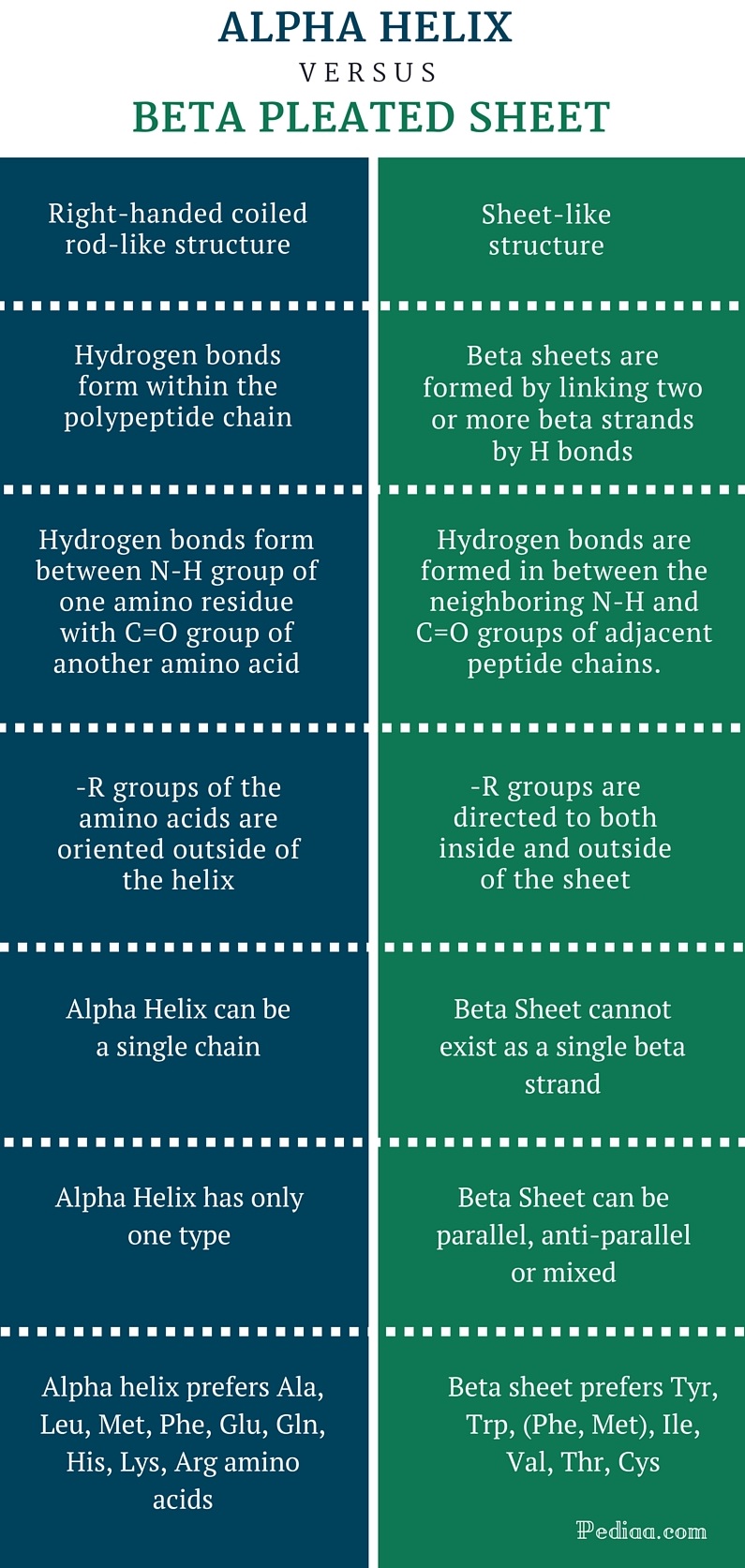
Difference Between Alpha Helix And Beta Pleated Sheet Alpha helix and beta pleated sheets are the common types of secondary protein structures. both structures are joined together by hydrogen bonds but differ in appearance and arrangement. Alpha helices are formed when the polypeptide chain twists into a spiral shape due to hydrogen bonds between the backbone amide and carbonyl groups. beta sheets, on the other hand, are created when adjacent segments of the polypeptide chain fold into a pleated, sheet like conformation, also stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
Comments are closed.