Deductive Vs Inductive Reasoning Key Differences Explained

Inductive Vs Deductive Reasoning Understand The Key Differences Deductive and inductive reasoning are both invaluable tools in critical thinking, problem solving, and decision making. understanding the key differences between them allows you to choose the right method depending on the situation at hand. Eight important differences between inductive and deductive reasoning are discussed in the article. inductive reasoning considers events for making the generalization. in contrast, deductive reasoning takes general statements as a base to arrive at a particular conclusion.

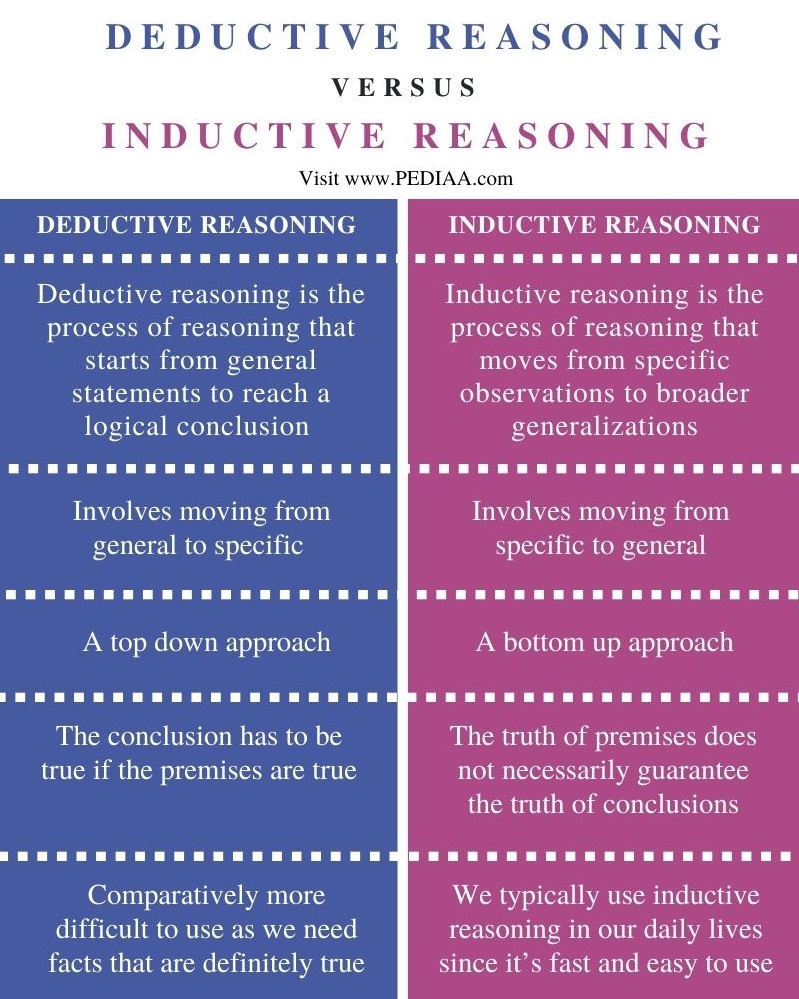
Inductive Vs Deductive Reasoning Useful Differences Inductive reasoning: allows you to reach a conclusion based on a specific observation. deductive reasoning: allows you to reach a conclusion based on a generalized premise. There are two different types of logical reasoning, namely deductive and inductive reasoning. deductive reasoning, or deduction, relies on general principles to derive specific. The main difference between inductive and deductive reasoning is that inductive reasoning aims at developing a theory while deductive reasoning aims at testing an existing theory. inductive reasoning moves from specific observations to broad generalisations, and deductive reasoning the other way around. Deductive reasoning involves applying a general rule to a specific case to reach a guaranteed conclusion, while inductive reasoning involves making generalizations based on specific examples or patterns.

Deductive Inductive Reasoning Definition Differences Example The main difference between inductive and deductive reasoning is that inductive reasoning aims at developing a theory while deductive reasoning aims at testing an existing theory. inductive reasoning moves from specific observations to broad generalisations, and deductive reasoning the other way around. Deductive reasoning involves applying a general rule to a specific case to reach a guaranteed conclusion, while inductive reasoning involves making generalizations based on specific examples or patterns. Deductive reasoning begins with a first premise, which is followed by a second premise and an inference, or a conclusion based on reasoning and evidence. a common form of deductive. In simple terms, this type of reasoning relies on evidence to support its premises. the opposite is starting with a premise and using logical rules to come up with a conclusion (deductive reasoning). inductive reasoning is appropriate to use in situations when there isn’t enough information. Explore the key differences between inductive and deductive reasoning, their applications in research and daily life, and how to use these critical thinking skills for better decision making. short on time? get instant insights with an ai summary of this post. The main difference between deductive reasoning and inductive reasoning lies in the approach used to reach conclusions. deductive reasoning starts with a general premise and applies it to specific cases, leading to conclusions that are logically certain if the premises hold true.
Inductive Deductive Reasoning 45 Off Www Micoope Gt Deductive reasoning begins with a first premise, which is followed by a second premise and an inference, or a conclusion based on reasoning and evidence. a common form of deductive. In simple terms, this type of reasoning relies on evidence to support its premises. the opposite is starting with a premise and using logical rules to come up with a conclusion (deductive reasoning). inductive reasoning is appropriate to use in situations when there isn’t enough information. Explore the key differences between inductive and deductive reasoning, their applications in research and daily life, and how to use these critical thinking skills for better decision making. short on time? get instant insights with an ai summary of this post. The main difference between deductive reasoning and inductive reasoning lies in the approach used to reach conclusions. deductive reasoning starts with a general premise and applies it to specific cases, leading to conclusions that are logically certain if the premises hold true.
Comments are closed.