Deductive Inductive Reasoning Definition Differences Example

Deductive Inductive Reasoning Definition Differences Example What is the difference between inductive vs. deductive reasoning? inductive reasoning involves starting from specific premises and forming a general conclusion, while deductive reasoning involves using general premises to form a specific conclusion. Inductive reasoning: allows you to reach a conclusion based on a specific observation. deductive reasoning: allows you to reach a conclusion based on a generalized premise.
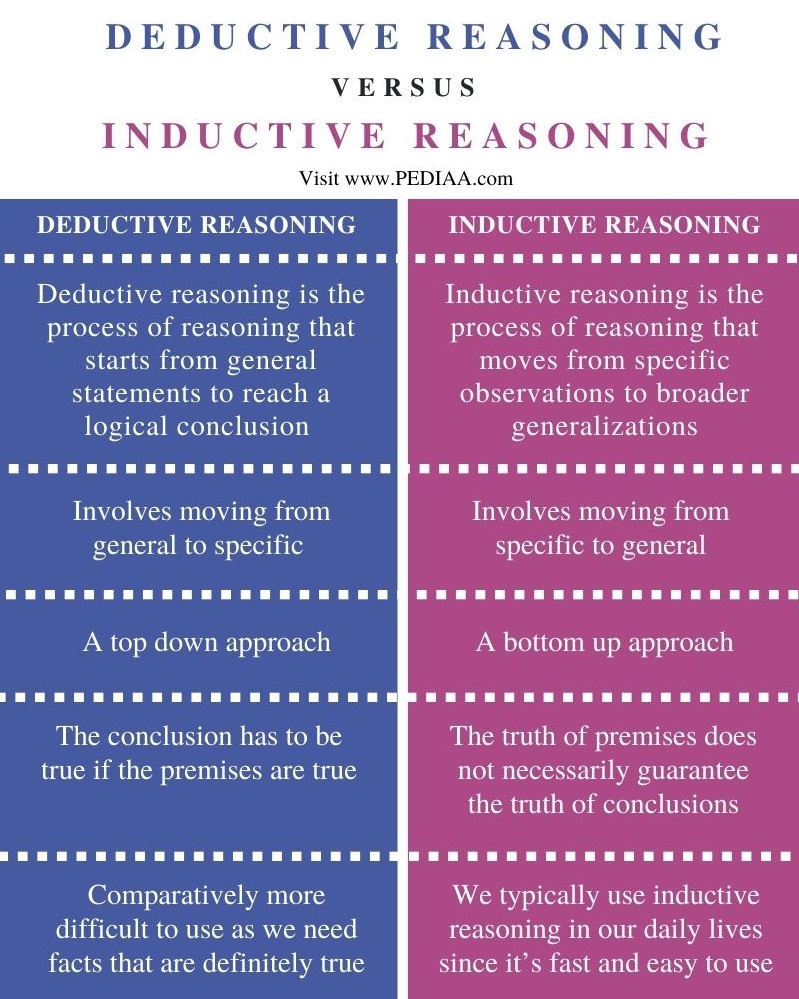
Inductive Deductive Reasoning 45 Off Www Micoope Gt The main difference between inductive and deductive reasoning is that inductive reasoning aims at developing a theory while deductive reasoning aims at testing an existing theory. Deductive reasoning, or deduction, is making an inference based on widely accepted facts or premises. if a beverage is defined as "drinkable through a straw," one could use deduction to determine soup to be a beverage. inductive reasoning, or induction, is making an inference based on an observation, and often an observation of a sample. Deductive reasoning means a form of logic in which specific inferences are drawn from multiple premises (general statements). it establishes the relationship between the proposition and conclusion. when all the proposed statements are true, then the rules of deduction are applied and the result obtained is inevitably true. Discover the key differences between inductive and deductive reasoning, their applications in critical thinking, and how they enhance decision making skills.
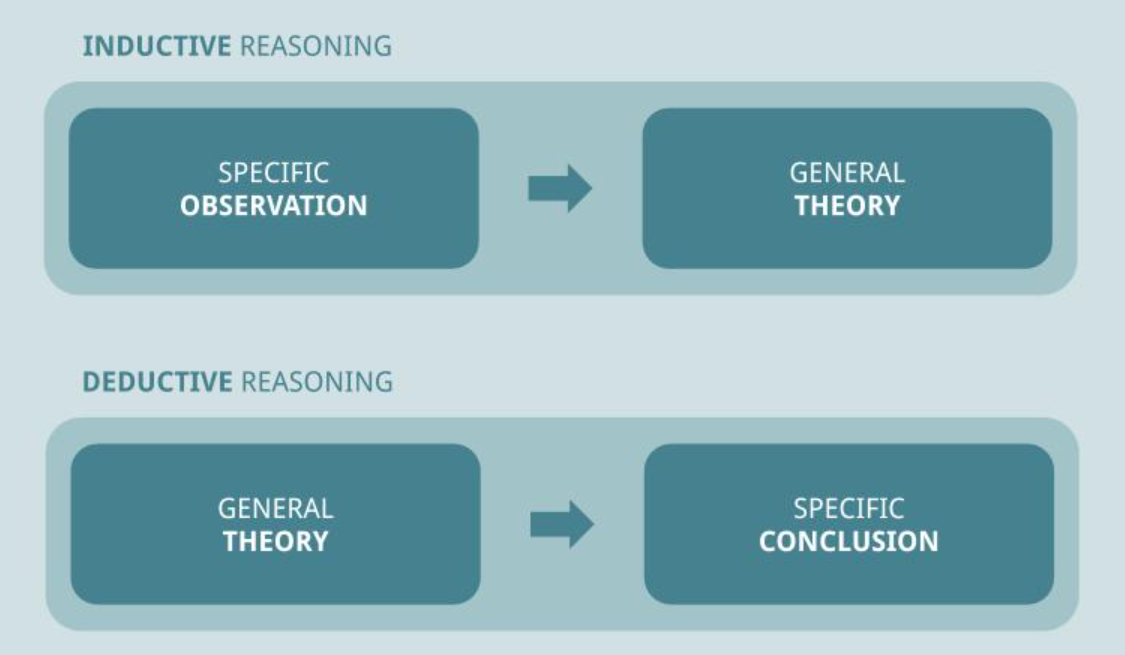
Deductive Inductive Reasoning Examples Differences Analytics Yogi Deductive reasoning means a form of logic in which specific inferences are drawn from multiple premises (general statements). it establishes the relationship between the proposition and conclusion. when all the proposed statements are true, then the rules of deduction are applied and the result obtained is inevitably true. Discover the key differences between inductive and deductive reasoning, their applications in critical thinking, and how they enhance decision making skills. Deductive reasoning and inductive reasoning are easy to mix up. learn what the difference is and see examples of each type of scientific reasoning. Deductive and inductive reasoning are both invaluable tools in critical thinking, problem solving, and decision making. understanding the key differences between them allows you to choose the right method depending on the situation at hand. There are two different types of logical reasoning, namely deductive and inductive reasoning. deductive reasoning, or deduction, relies on general principles to derive specific. Inductive reasoning relies on patterns and trends, while deductive reasoning relies on facts and rules. inductive reasoning follows a flow from specific to general, deductive reasoning flows from general to specific. you might use inductive reasoning to understand how something works by observing patterns.
Comments are closed.