Consumer Surplus Under Monopoly
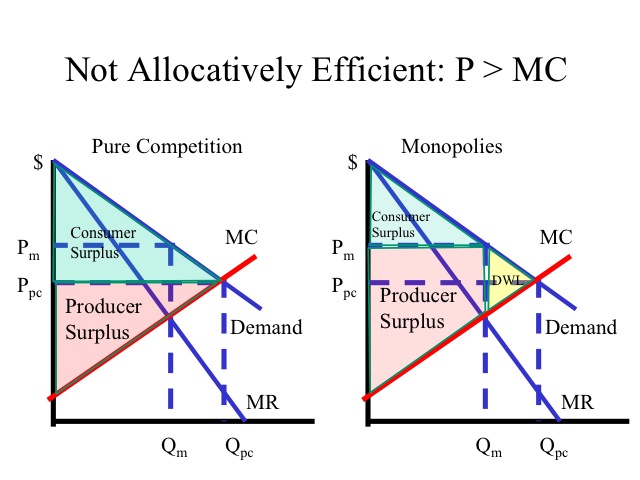
Monopoly Graph Consumer Surplus With monopoly, consumer surplus would be the area below the demand curve and above p m r. part of the reduction in consumer surplus is the area under the demand curve between q c and q m; it is contained in the deadweight loss area grc. but consumers also lose the area of the rectangle bounded by the competitive and monopoly prices and by the. Consumer surplus equals the area of the under the demand curve and monopoly price (p m), horizontal line. coordinates of three corners of this triangle will be: top left: (0, demand curve intercept) = (0, 140).

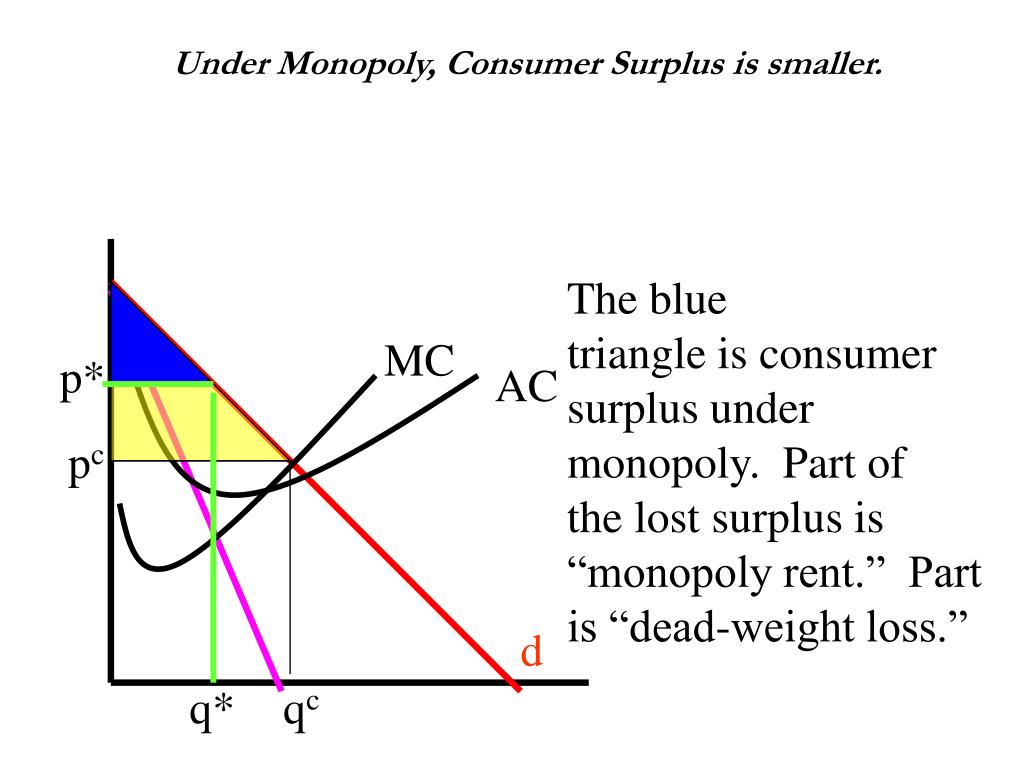
B Producer Surplus Under Monopoly Is Larger By How Much In that case, consumer surplus is area cs. when price drops to p 1, quantity sold increases. on the one hand, there is an increase on the consumer surplus of initial consumers, being this equal to area cs’. on the other hand, new consumers are willing to buy, being their consumer surplus ncs. producer surplus:. Higher prices higher price and lower output than under perfect competition. this leads to a decline in consumer surplus and a deadweight welfare loss; allocative inefficiency. a monopoly is allocatively inefficient because in monopoly the price is greater than mc. p > mc. in a competitive market, the price would be lower and more consumers. How to illustrate the area of consumer surplus under a monopoly and how it compares to consumer surplus under a perfectly competitive market. – in a monopoly, consumer surplus is always lower (relative to perfect competition). – but it could be that the increase in the firm’s profit more than o↵sets the decrease in consumer surplus. lower! illustrate graphically. (example with linear demand and marginal cost func tions.) under monopoly pricing: – the firm sets p.
-crop-1598895869331.png?1598895869)
Monopoly Graph Consumer Surplus How to illustrate the area of consumer surplus under a monopoly and how it compares to consumer surplus under a perfectly competitive market. – in a monopoly, consumer surplus is always lower (relative to perfect competition). – but it could be that the increase in the firm’s profit more than o↵sets the decrease in consumer surplus. lower! illustrate graphically. (example with linear demand and marginal cost func tions.) under monopoly pricing: – the firm sets p. Market surplus = $4.2 billion monopoly market. in comparison, the monopoly market has p e = $140 and q e = 30 million. figure 8.1h. calculating market surplus: consumer surplus = $900 million. blue shaded region. [($200 $140)*(30)] 2 = 900 million. notice consumer surplus decreased for two reasons. We therefore see higher prices and lower quantities under monopoly than under perfect competition: p m>p cand q m<q c. as a result, some socially desirable transactions don’t happen. these missing trades are missed opportunities to expand the economic pie. de ning total surplus as the sum of consumer and producer surplus, we’ll see that.

Monopoly Market surplus = $4.2 billion monopoly market. in comparison, the monopoly market has p e = $140 and q e = 30 million. figure 8.1h. calculating market surplus: consumer surplus = $900 million. blue shaded region. [($200 $140)*(30)] 2 = 900 million. notice consumer surplus decreased for two reasons. We therefore see higher prices and lower quantities under monopoly than under perfect competition: p m>p cand q m<q c. as a result, some socially desirable transactions don’t happen. these missing trades are missed opportunities to expand the economic pie. de ning total surplus as the sum of consumer and producer surplus, we’ll see that.
Ppt Duffy S Notes Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 4365824

Comments are closed.