Chapter 5 Section 4_exponential Log Equations 1_part A

Unit 4 Exponential And Logarithmic Functions Pdfdrive Pdf Converting between exponential and logarithmic form example 1. in each part, write the exponential equation in its equivalent logarithmic form. a. 2 10x log 2. Use properties of logarithms to combine all logarithms and write as a single logarithm if needed. use the definition of a logarithmic function to rewrite the equation in exponential form. solve for the given variable. check for any extraneous solutions.

Log And Exponential Equations Example 1 5 X 5 2 3 59 In chapter 4 we studied functions of the form where is any real number. now we are going to turn our attention, in section 5.2, to a group of functions where the variable is in the exponent, rather than the base. Steps to solving logarithmic equations. This chapter reviews these laws before recalling exponential functions. then it explores inverses of exponential functions, which are called logarithms. recall that in an expression such as an in which a is raised to the power of n, the number a is called the base and n is the exponent. E notation used to emphasize the fact that it is a function. in accordance with the idea of corresponding input and output values, these equations are oft represented with the notation f ( x ) for the output value. this notation is read as “ f of x ”.

Mac 1105 4 4 Exponential Log Equations 4 Exponential This chapter reviews these laws before recalling exponential functions. then it explores inverses of exponential functions, which are called logarithms. recall that in an expression such as an in which a is raised to the power of n, the number a is called the base and n is the exponent. E notation used to emphasize the fact that it is a function. in accordance with the idea of corresponding input and output values, these equations are oft represented with the notation f ( x ) for the output value. this notation is read as “ f of x ”. C h a p t e r 5 logarithmic, exponential, and other transcendental functions section 5.1 the natural logarithmic function: differentiation 1. for x 1, ln x =. Solving exponential and logarithmic equations a solving exponential and logarithmic equations a from larson texts, inc. on vimeo. 5.4 exponential functions: differentiation and integration develop properties of the natural exponential function. differentiate natural exponential functions. integrate natural exponential functions. In this section, you will study procedures for solving equations involving exponential and logarithmic expressions. there are two basic strategies for solving exponential or logarithmic equations.

Exponential And Logarithmic Functions Review And Preview Of Course Hero C h a p t e r 5 logarithmic, exponential, and other transcendental functions section 5.1 the natural logarithmic function: differentiation 1. for x 1, ln x =. Solving exponential and logarithmic equations a solving exponential and logarithmic equations a from larson texts, inc. on vimeo. 5.4 exponential functions: differentiation and integration develop properties of the natural exponential function. differentiate natural exponential functions. integrate natural exponential functions. In this section, you will study procedures for solving equations involving exponential and logarithmic expressions. there are two basic strategies for solving exponential or logarithmic equations.
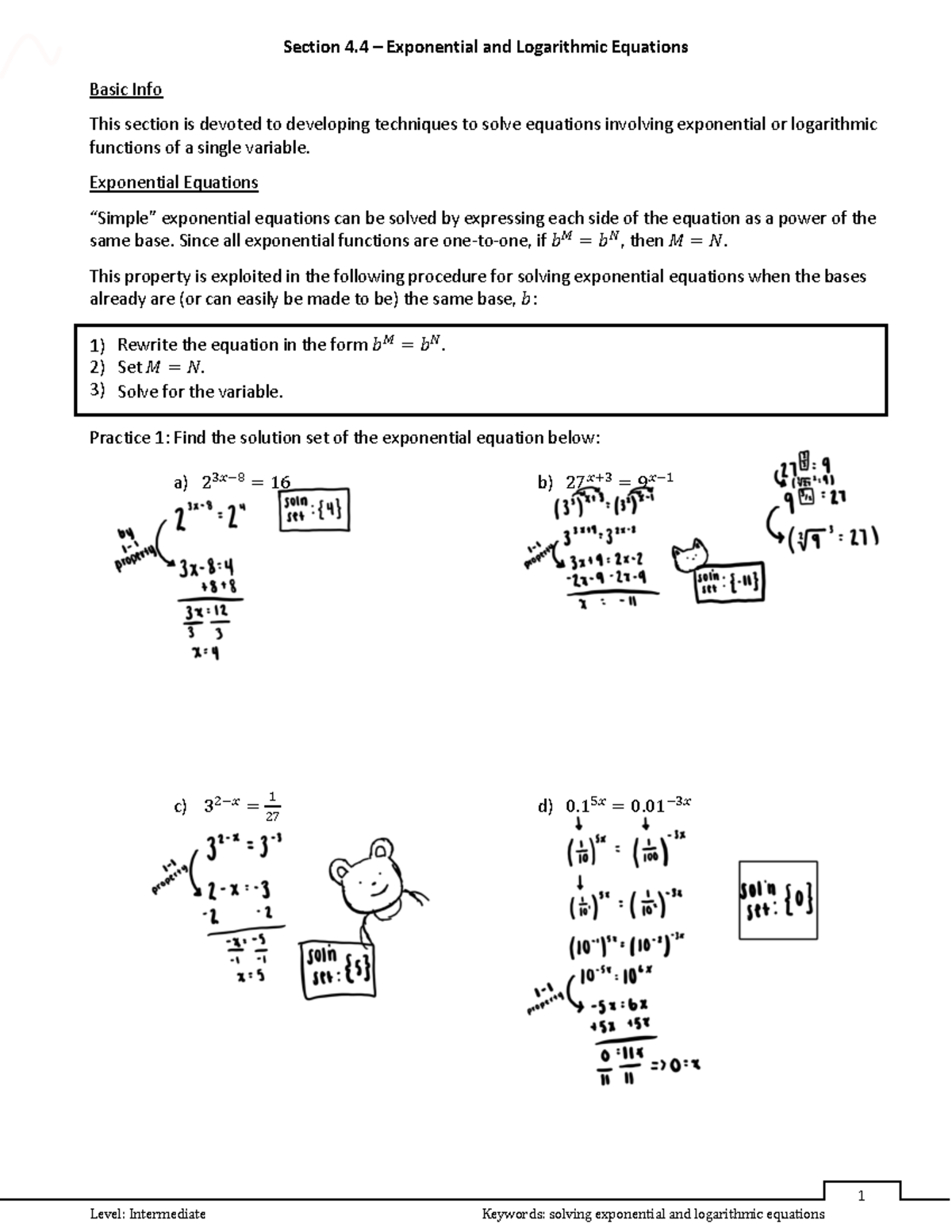
4 4 Exponential And Logarithmic Equations 1 Basic Info This Section 5.4 exponential functions: differentiation and integration develop properties of the natural exponential function. differentiate natural exponential functions. integrate natural exponential functions. In this section, you will study procedures for solving equations involving exponential and logarithmic expressions. there are two basic strategies for solving exponential or logarithmic equations.
Comments are closed.