According To Behavioral Economics Consumers

According To Behavioral Economicsвђ Consumers According to behavioral economics, consumers a. always behave rationally because they account for sunk costs. b. always behave rationally because they take into account monetary costs and non monetary opportunity costs. c. do not always behave rationally because they take into account non monetary opportunity costs. According to behavioral economics, consumers. do not always behave rationally because they. are overly optimistic about their future behavior. three common mistakes made by consumers are: taking into account monetary costs but ignoring nonmonetary opportunity costs. failing to ignore sunk costs.
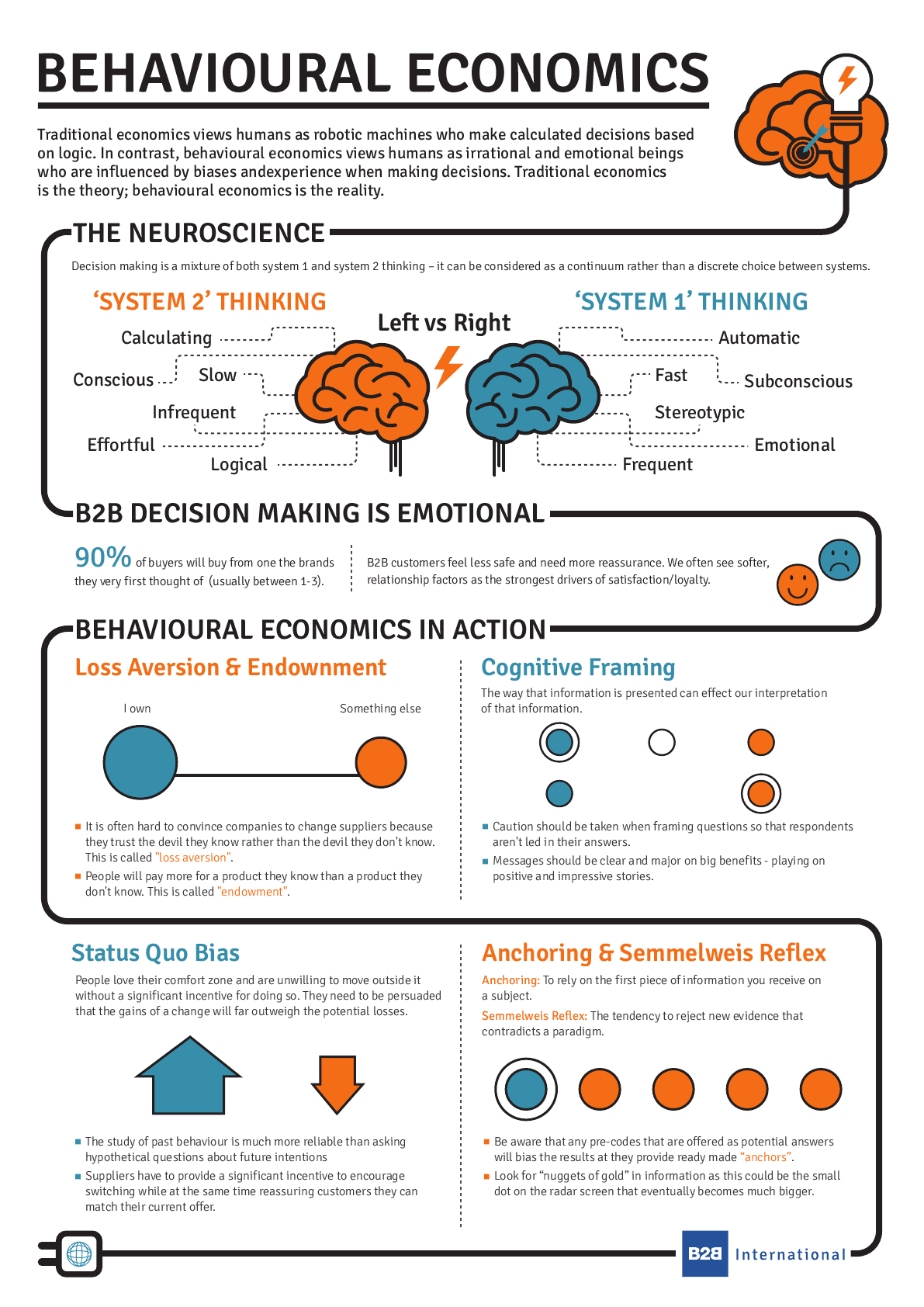
What Is Behavioural Economics Infographic B2b International According to behavioral economics, consumers a. do not always behave rationally because they take into account nonmonetary opportunity costs. b. always behave rationally because they take into account monetary costs and nonmonetary opportunity costs. c. do not always behave rationally because they fail to ignore sunk costs. d. Making choices. in what category did consumers worldwide increase their spending during the great recession? higher education. according to the united nations educational, scientific, and cultural organization (unesco), enrollment in colleges and universities rose one third in china and almost two thirds in saudi arabia, nearly doubled in pakistan, tripled in uganda, and surged by three. Making choices. in what category did consumers worldwide increase their spending during the great recession? higher education. according to the united nations educational, scientific, and cultural organization (unesco), enrollment in colleges and universities rose one third in china and almost two thirds in saudi arabia, nearly doubled in pakistan, tripled in uganda, and surged by three. 5.4. behavioral economics: an alternative viewpoint. as we know, people sometimes make decisions that seem "irrational" and not in their own best interest. people's decisions can seem inconsistent from one day to the next and they even deliberately ignore ways to save money or time. the traditional economic models assume rationality, which.

Ten Consumer Behaviour Models Short Notes Bba Mantra Making choices. in what category did consumers worldwide increase their spending during the great recession? higher education. according to the united nations educational, scientific, and cultural organization (unesco), enrollment in colleges and universities rose one third in china and almost two thirds in saudi arabia, nearly doubled in pakistan, tripled in uganda, and surged by three. 5.4. behavioral economics: an alternative viewpoint. as we know, people sometimes make decisions that seem "irrational" and not in their own best interest. people's decisions can seem inconsistent from one day to the next and they even deliberately ignore ways to save money or time. the traditional economic models assume rationality, which. Behavioral economics is the merger of microeconomic principles with the procedures and principles of the experimental analysis of behavior. this review describes two branches of behavioral economic research: variables affecting decision making and consumer demand. each branch is discussed with an eye toward identifying behavioral economic principles that will be of utility to those tasked with. Glossary. behavioral economics. a branch of economics that seeks to enrich the understanding of decision making by integrating the insights of psychology and by investigating how given dollar amounts can mean different things to individuals depending on the situation. fungible.

What Is Behavioral Economics Your Quick Guide Slidemodel Behavioral economics is the merger of microeconomic principles with the procedures and principles of the experimental analysis of behavior. this review describes two branches of behavioral economic research: variables affecting decision making and consumer demand. each branch is discussed with an eye toward identifying behavioral economic principles that will be of utility to those tasked with. Glossary. behavioral economics. a branch of economics that seeks to enrich the understanding of decision making by integrating the insights of psychology and by investigating how given dollar amounts can mean different things to individuals depending on the situation. fungible.

Ppt Consumer Equilibrium And Market Demand Powerpoint Presentation

Comments are closed.