08 Class Inheritance Pdf Inheritance Object Oriented Programming

Object Oriented Programming Inheritance Pdf Inheritance Object This chapter continues our discussion of object oriented programming (oop) by intro ducing inheritance, in which a new class is created by acquiring an existing class’s mem bers and possibly embellishing them with new or modified capabilities. Our objectives are as follows: implement base classes. implement derived classes. initialize base classes from derived classes. learn how to call base class members. learn how to hide base class members. programming. it allows you to reuse existing code. through effective. employment of reuse, you can save time in your programming. listing 8 1.

Object Oriented Programming Class Objects And Inheritance Download With inheritance, we can define a superclass named creature that abstracts the shared attributes and methods. we can then define player and monster as subclasses of creature. example: refactoring the player class. when creating subclasses, a common pattern calls for redefining methods. Inheritance what is inheritance? complete the guided notes on the unit 1 guide. inheritance is an object oriented programming principle where a subclass inherits the attributes and behaviors of a superclass. The class that does the inheriting is called asub class. therefore, a sub class is a specialized version of a super class. it inherits all of the variables, methods etc defined by the super class and add its own unique elements. the idea of inheritance implements the is a relationship. for example, general syntax someclass super class { …. Introduc tion abstraction focus on commonalities among objects in system “is a” vs. “has a” “is a” inheritance subclass object treated as superclass object example: car is a vehicle vehicle properties behaviors also car properties behaviors “has a” composition object contains one or more objects of other classes as members.
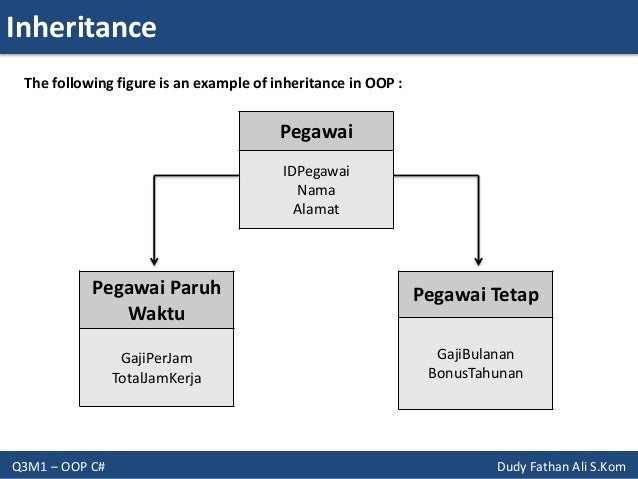
Object Oriented Programming Inheritance The class that does the inheriting is called asub class. therefore, a sub class is a specialized version of a super class. it inherits all of the variables, methods etc defined by the super class and add its own unique elements. the idea of inheritance implements the is a relationship. for example, general syntax someclass super class { …. Introduc tion abstraction focus on commonalities among objects in system “is a” vs. “has a” “is a” inheritance subclass object treated as superclass object example: car is a vehicle vehicle properties behaviors also car properties behaviors “has a” composition object contains one or more objects of other classes as members. Inheritance in object oriented programs, we use inheritance as one way to reuse program code. in java, if class b extends class a, then b inherits (receives) all methods and fields from a. class b does not have to redefine these fields or methods. class a is called the superclass (or parent class). class b is called the subclass (or child class). Object oriented programming: inheritance object oriented programming paradigm: represent programs as a set of objects that encapsulate data and methods (state and behaviour) and pass messages between one another. Object oriented software engineering: using uml, patterns, and java 30! f when should you use these design patterns? • a façade should be offered by all subsystems in a software system who a services • the adapter design pattern should be used to interface to existing components • the bridge design pattern should be used to. Inheritance inheritance is a powerful feature in object oriented programming it refers to defining a new class with little or no modification to an existing class. the new class is called derived (or child) class and the one from which it inherits is called the base (or parent) class.

Understanding Inheritance In Object Oriented Programming Inheritance in object oriented programs, we use inheritance as one way to reuse program code. in java, if class b extends class a, then b inherits (receives) all methods and fields from a. class b does not have to redefine these fields or methods. class a is called the superclass (or parent class). class b is called the subclass (or child class). Object oriented programming: inheritance object oriented programming paradigm: represent programs as a set of objects that encapsulate data and methods (state and behaviour) and pass messages between one another. Object oriented software engineering: using uml, patterns, and java 30! f when should you use these design patterns? • a façade should be offered by all subsystems in a software system who a services • the adapter design pattern should be used to interface to existing components • the bridge design pattern should be used to. Inheritance inheritance is a powerful feature in object oriented programming it refers to defining a new class with little or no modification to an existing class. the new class is called derived (or child) class and the one from which it inherits is called the base (or parent) class.

Inheritance In C Object Oriented Programming Object oriented software engineering: using uml, patterns, and java 30! f when should you use these design patterns? • a façade should be offered by all subsystems in a software system who a services • the adapter design pattern should be used to interface to existing components • the bridge design pattern should be used to. Inheritance inheritance is a powerful feature in object oriented programming it refers to defining a new class with little or no modification to an existing class. the new class is called derived (or child) class and the one from which it inherits is called the base (or parent) class.
Comments are closed.